Citrate
First intermediate of the Krebs cycle. Also shuttles acetyl-CoA from mitochondria for fat synthesis.

Citrate (citric acid) is the first intermediate of the Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle), formed when acetyl-CoA condenses with oxaloacetate via citrate synthase. This six-carbon molecule is subsequently processed through the cycle to generate energy.
Beyond energy production, citrate serves as a key metabolic signal and shuttle: When cellular energy is high, citrate accumulates and is exported from mitochondria. In the cytoplasm, ATP-citrate lyase cleaves it back to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. This cytoplasmic acetyl-CoA is used for fatty acid synthesis and cholesterol synthesis.
Citrate inhibits phosphofructokinase (PFK), a key glycolytic enzyme - when energy is abundant, this slows glucose breakdown. It also activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase, promoting fat synthesis when energy is plentiful. Citrate binds calcium and other minerals in urine, preventing kidney stone formation.
Potassium citrate supplementation is used to prevent calcium oxalate and uric acid kidney stones. Citrate also enhances mineral absorption when used as mineral salt forms (magnesium citrate, calcium citrate). In the context of metabolic dysfunction, impaired citrate cycle flow (from nutrient deficiencies or mitochondrial issues) can limit energy production and cause citrate to back up or be diverted inappropriately.
Metabolic Connections
Citrate connects to 4 other pathways.
Metabolites

Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate, the first step of the Krebs cycle
Central metabolite linking carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Entry point to Krebs cycle for energy production.

Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate, the first step of the Krebs cycle
Central metabolite linking carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Entry point to Krebs cycle for energy production.
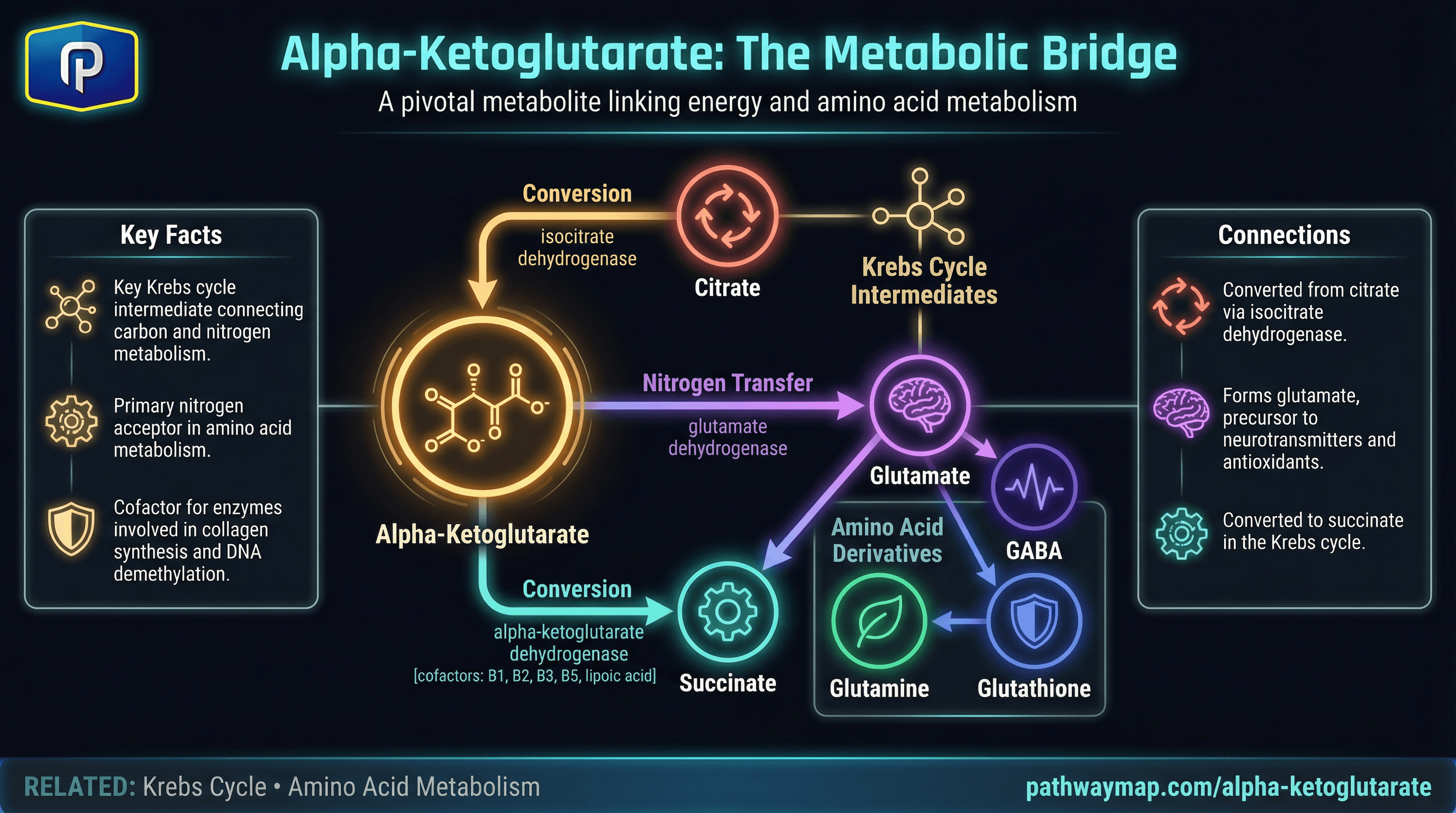
Alpha-Ketoglutarate
Both are Krebs cycle intermediates; citrate is converted through isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate
Krebs cycle intermediate bridging energy metabolism with amino acid synthesis. Precursor to glutamate.

Alpha-Ketoglutarate
Both are Krebs cycle intermediates; citrate is converted through isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate
Krebs cycle intermediate bridging energy metabolism with amino acid synthesis. Precursor to glutamate.