Phosphatidylcholine
Major phospholipid in cell membranes and primary component of bile. Essential for liver function and fat transport.
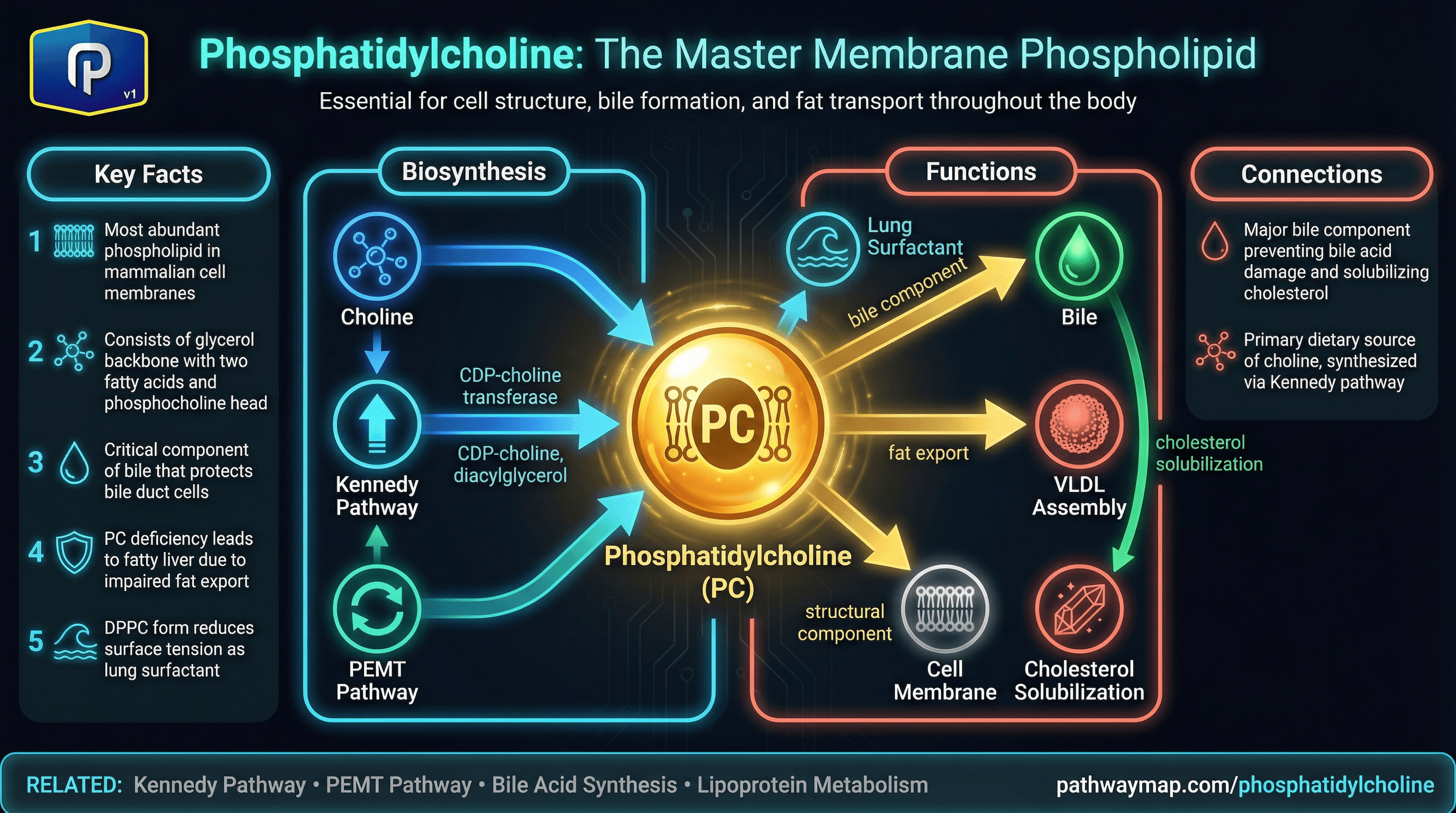
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is the most abundant phospholipid in mammalian cell membranes and a critical component of bile and lipoproteins.
It is synthesized from choline via the Kennedy pathway or from phosphatidylethanolamine via the PEMT pathway. Structure: PC consists of a glycerol backbone with two fatty acids and a phosphocholine head group. The fatty acid composition varies, affecting membrane properties.
Functions: Cell membrane structure (major component, affecting fluidity and signaling), Bile constituent (prevents bile acids from damaging bile duct cells; required for cholesterol solubilization), Lipoprotein component (essential for VLDL assembly and fat export from liver), Lung surfactant (DPPC, a saturated PC, reduces surface tension), and Choline source (PC is the main dietary choline form).
PC and liver health: The liver requires PC to package and export fats as VLDL. PC deficiency leads to fat accumulation (fatty liver). This is why choline deficiency causes fatty liver. PC in bile: Without adequate PC, bile acids damage biliary epithelium.
PC also keeps cholesterol solubilized in bile; low PC contributes to gallstone formation. Dietary and supplemental sources: Eggs, liver, and soybeans are rich in PC. Lecithin supplements are primarily PC. Supplemental forms include soy lecithin, sunflower lecithin, and purified PC.
PC is sometimes used therapeutically for: liver support, gallbladder health, cognitive function (as choline source), and cell membrane support.
Metabolic Connections
Phosphatidylcholine connects to 5 other pathways.
Digestive Factors

Bile
Phosphatidylcholine is a major component of bile, protecting bile ducts and solubilizing cholesterol
Digestive fluid produced by liver, stored in gallbladder. Essential for fat digestion and toxin elimination.

Bile
Phosphatidylcholine is a major component of bile, protecting bile ducts and solubilizing cholesterol
Digestive fluid produced by liver, stored in gallbladder. Essential for fat digestion and toxin elimination.
Cellular Structures
Nutrients

Choline
Phosphatidylcholine is the main dietary form of choline and a major membrane phospholipid
Essential nutrient for brain development, liver function, and methylation via the BHMT pathway.

Choline
Choline is incorporated into phosphatidylcholine, a major membrane phospholipid
Essential nutrient for brain development, liver function, and methylation via the BHMT pathway.
