Cell Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer surrounding cells; contains proteins, cholesterol; regulates transport and signaling.

Cell membranes are phospholipid bilayers that surround all cells and organelles, creating compartmentalized environments essential for life.
The primary phospholipids are phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin. Cholesterol modulates membrane fluidity. Membrane proteins handle transport (channels, carriers, pumps), signaling (receptors), and cell identity (antigens).
Membrane fatty acid composition affects fluidity and function - omega-3s increase fluidity while saturated fats decrease it.
Membrane synthesis
choline
serine
ethanolamine
fatty acids
cholesterol
methylation (for PC synthesis via PEMT).
Mitochondrial membranes have unique lipid composition including cardiolipin. Membrane damage from oxidation or toxins impairs cellular function.
Metabolic Connections
Cell Membrane connects to 6 other pathways.
Cell Membrane

Cholesterol
Cholesterol regulates membrane fluidity and stability
Essential sterol in cell membranes. Precursor to all steroid hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids.
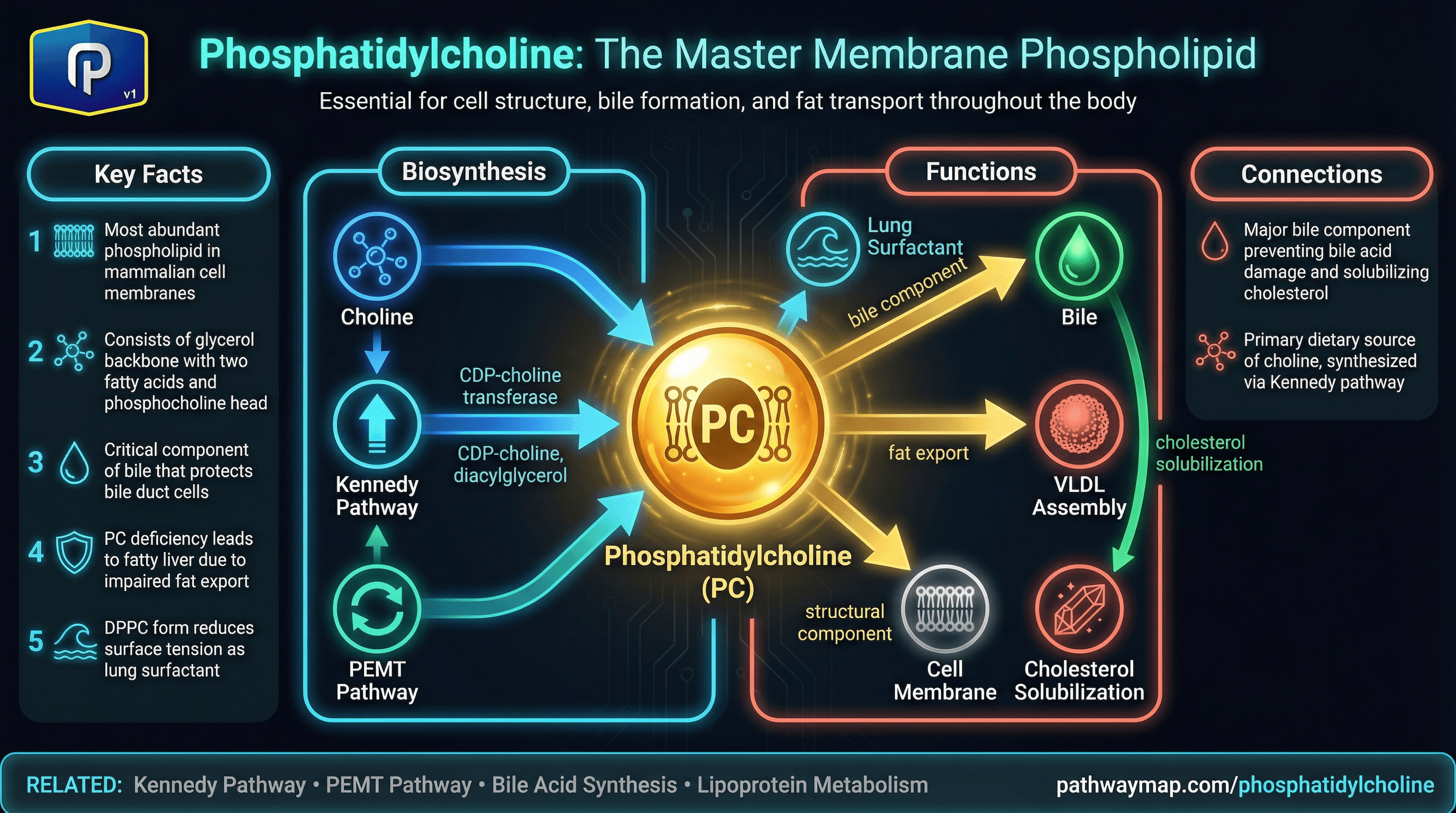
Phosphatidylcholine
PC is the most abundant membrane phospholipid
Major phospholipid in cell membranes and primary component of bile. Essential for liver function and fat transport.
Fatty Acids

Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids in membranes increase fluidity and anti-inflammatory signaling
Essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (EPA, DHA, ALA); anti-inflammatory; critical for brain and heart health.

Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s (especially DHA) are incorporated into cell membranes, affecting fluidity and function
Essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (EPA, DHA, ALA); anti-inflammatory; critical for brain and heart health.

