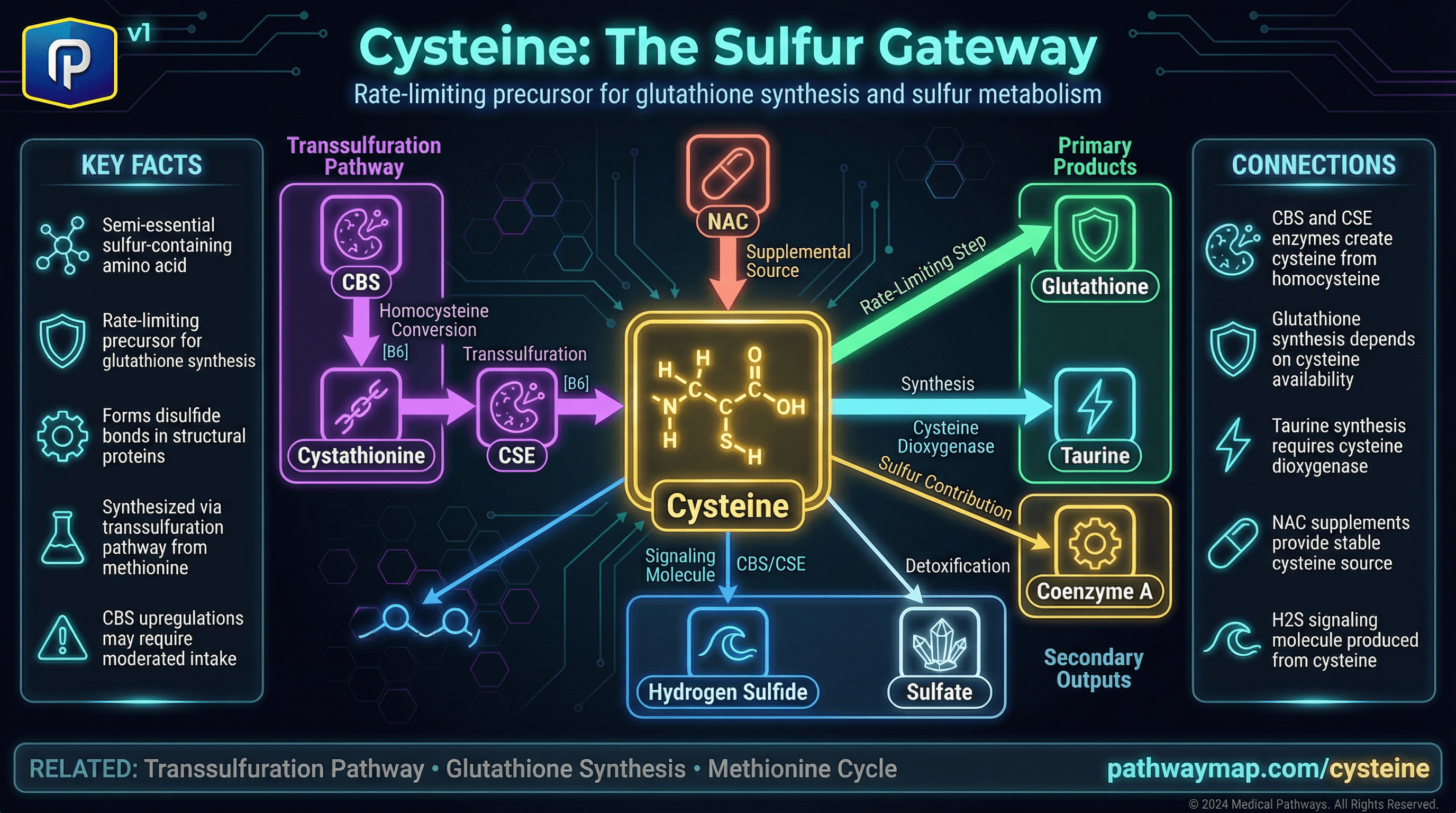
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
Gasotransmitter produced by transsulfuration enzymes; regulates blood pressure, inflammation, and mitochondrial function.

Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a gaseous signaling molecule produced primarily by the transsulfuration enzymes CBS and CSE, as well as by 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST). Despite its reputation as a toxic gas, endogenous H2S at physiological concentrations has important beneficial effects: vasodilation (lowering blood pressure), anti-inflammatory actions, antioxidant effects (by increasing glutathione), and regulation of mitochondrial bioenergetics.
H2S can inhibit cytochrome c oxidase at high concentrations but may enhance mitochondrial ATP production at low concentrations. H2S also promotes angiogenesis, inhibits platelet aggregation, and may protect against neurodegeneration. Garlic's health benefits are partly attributed to H2S-releasing compounds.
Metabolic Connections
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) connects to 8 other pathways.
Physiological Parameters

Blood Pressure
H2S causes vasodilation and lowers blood pressure
Force of blood against artery walls; regulated by nervous, renal, and endocrine systems; affected by many nutrients.

Blood Pressure
H2S is a vasodilator that helps regulate blood pressure
Force of blood against artery walls; regulated by nervous, renal, and endocrine systems; affected by many nutrients.
Enzymes

CSE (Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase)
CSE is a major enzymatic source of H2S production
Enzyme that cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine; B6 dependent; also produces hydrogen sulfide.

CSE (Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase)
CSE produces H2S as a signaling molecule from cysteine or homocysteine
Enzyme that cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine; B6 dependent; also produces hydrogen sulfide.