Cysteine
The bottleneck for glutathione. Your body's master antioxidant can only be made as fast as cysteine is available. This sulfur amino acid can be made from methionine or obtained from diet, with NAC being the most popular supplement form.
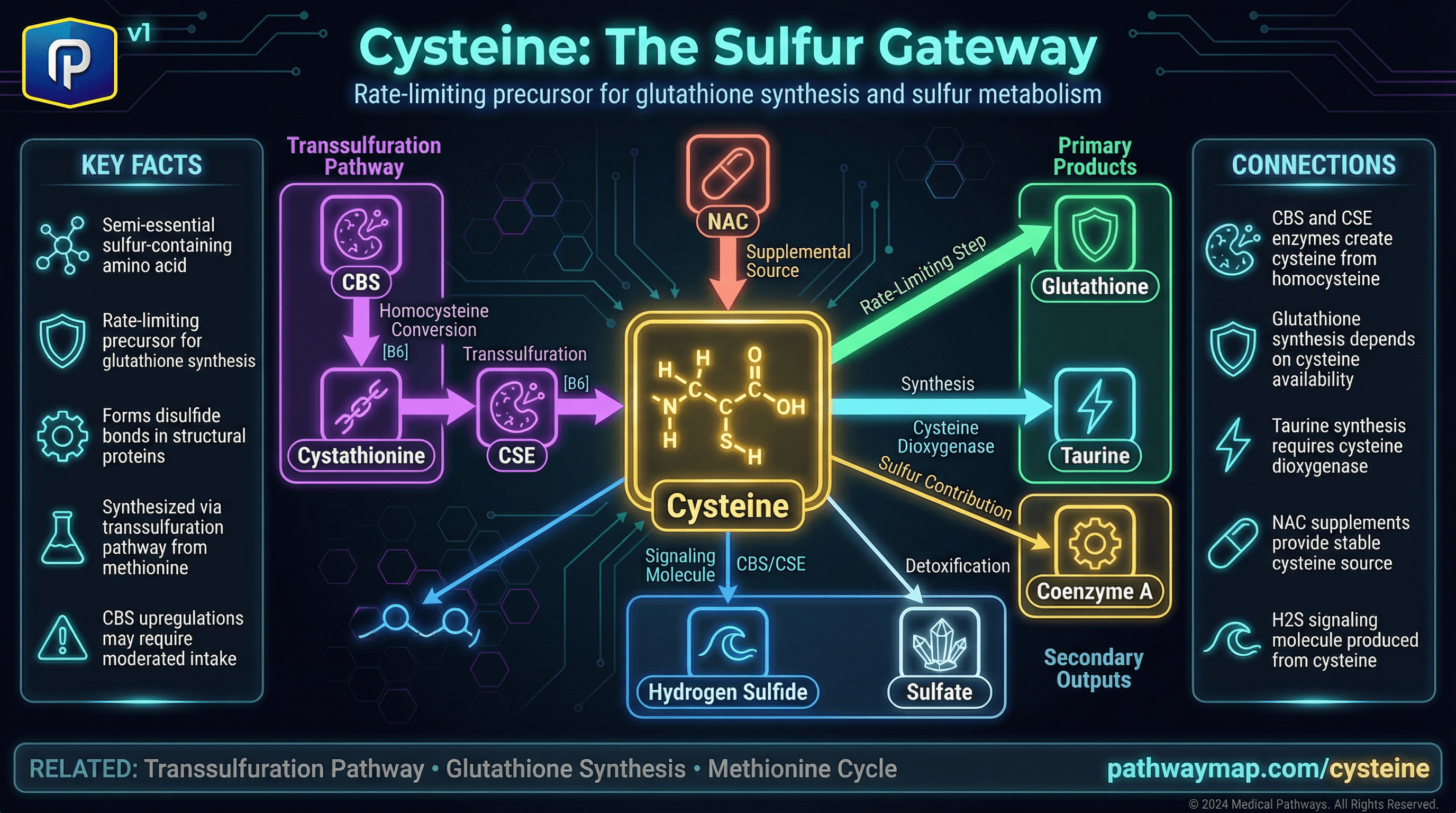
What Cysteine Does
Glutathione Synthesis
Rate-limiting component of glutathione (γ-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine). More cysteine = more glutathione.
Taurine Production
Converted to taurine via cysteine dioxygenase. Important for heart, brain, bile acids.
Disulfide Bonds
Forms structural cross-links in proteins. Critical for keratin (hair, nails), collagen stability.
Sulfate Production
Provides sulfate for Phase 2 sulfation detox and proteoglycan synthesis.
Coenzyme A
Cysteine contributes sulfur to CoA synthesis. Essential for energy metabolism.
Metallothionein
Cysteine-rich proteins that bind heavy metals for safe transport and storage.
Where Cysteine Comes From
Transsulfuration Pathway
Made from methionine when methylation is working well:
Dietary Sources
Direct from protein foods:
- • Eggs (high in cysteine)
- • Meat, poultry, fish
- • Dairy products
- • Garlic, onions (sulfur-rich)
- • Cruciferous vegetables
NAC (N-Acetylcysteine)
NAC is the acetylated form of cysteine - more stable and better absorbed than free cysteine. It's the most common way to supplement cysteine for glutathione support.
Glutathione Precursor
Provides cysteine for glutathione synthesis. Most effective oral GSH support.
Mucolytic
Breaks disulfide bonds in mucus, thinning it. Used for respiratory conditions.
Acetaminophen Antidote
IV NAC is the treatment for Tylenol overdose - rapidly restores glutathione.
NAC Dosing
- •General support: 600-1200mg daily
- •Respiratory: 600mg 2-3x daily
- •Take with vitamin C to prevent oxidation
- •Can chelate zinc/copper - consider supplementing
- •May cause GI upset if taken on empty stomach
Cysteine Cautions
CBS Upregulation
Some people have overactive CBS, shunting too much toward sulfur. They may not tolerate high cysteine/NAC.
Sulfur Sensitivity
Some individuals react to sulfur compounds with headaches, skin issues, or GI distress.
Histamine Connection
High sulfur intake may increase histamine in sensitive individuals via DAO inhibition.
Mineral Chelation
NAC can bind zinc and copper. Long-term high-dose use may require mineral supplementation.