CSE (Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase)
Enzyme that cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine; B6 dependent; also produces hydrogen sulfide.

Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase (CSE, also called CTH or CGL) is the second enzyme in the transsulfuration pathway, cleaving cystathionine to produce cysteine, alpha-ketobutyrate, and ammonia. Like CBS, CSE requires pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP, active B6) as a cofactor.
CSE is also a major source of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gasotransmitter with important roles in vasodilation, inflammation, and cellular signaling.
CSE can produce H2S from cysteine or homocysteine directly.
CSE deficiency leads to cystathioninuria but is generally considered benign. CSE expression is induced by ER stress and is important for maintaining cysteine pools for glutathione synthesis during oxidative stress.
Metabolic Connections
CSE (Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase) connects to 10 other pathways.
Metabolites

Ammonia
CSE releases ammonia when cleaving cystathionine to cysteine
Toxic nitrogen waste from amino acid metabolism; detoxified to urea in liver; elevated in liver disease.

Cystathionine
CSE cleaves cystathionine to release cysteine
Intermediate in transsulfuration pathway; formed from homocysteine and serine by CBS enzyme.

Cystathionine
CSE enzyme cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine
Intermediate in transsulfuration pathway; formed from homocysteine and serine by CBS enzyme.
B Vitamins

B6
B6 (as PLP) is required for CSE catalytic activity
Pyridoxine - essential for over 100 enzyme reactions including neurotransmitter synthesis and transsulfuration.

B6
B6 (as PLP) is required for CSE to cleave cystathionine to cysteine
Pyridoxine - essential for over 100 enzyme reactions including neurotransmitter synthesis and transsulfuration.
Amino Acids
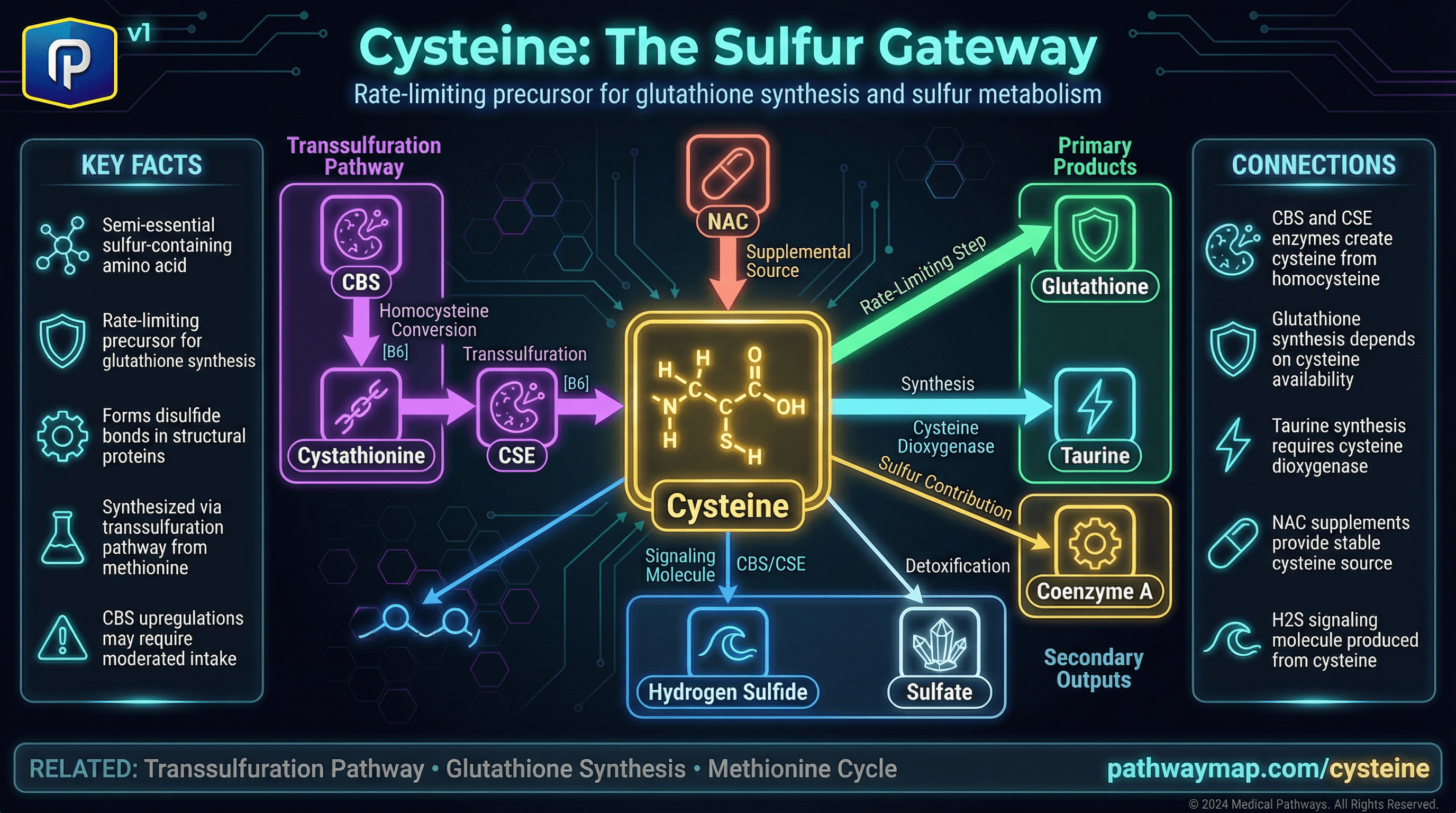
Cysteine
Cysteine is the main product of CSE, used for glutathione and protein synthesis
Sulfur-containing amino acid - rate-limiting precursor for glutathione synthesis.

Cysteine
Cysteine is produced from cystathionine by CSE enzyme
Sulfur-containing amino acid - rate-limiting precursor for glutathione synthesis.
Signaling Molecules

Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
CSE produces H2S as a signaling molecule from cysteine or homocysteine
Gasotransmitter produced by transsulfuration enzymes; regulates blood pressure, inflammation, and mitochondrial function.

Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
CSE is a major enzymatic source of H2S production
Gasotransmitter produced by transsulfuration enzymes; regulates blood pressure, inflammation, and mitochondrial function.
