Cystathionine
Intermediate in transsulfuration pathway; formed from homocysteine and serine by CBS enzyme.

Cystathionine is a key intermediate in the transsulfuration pathway that converts homocysteine to cysteine. It is formed when cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) combines homocysteine with serine in a B6-dependent reaction. Cystathionine is then cleaved by cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE/CTH), also B6-dependent, to produce cysteine, alpha-ketobutyrate, and ammonia.
This pathway is irreversible and represents the major route for homocysteine disposal when methionine is abundant. Cystathionine levels are very low in normal plasma because it is rapidly converted to cysteine. Elevated cystathionine indicates either CBS overactivity or CSE deficiency.
The transsulfuration pathway also produces hydrogen sulfide (H2S), an important signaling molecule.
Metabolic Connections
Cystathionine connects to 12 other pathways.
B Vitamins

B6
Both CBS and CSE require B6 (PLP) as a cofactor
Pyridoxine - essential for over 100 enzyme reactions including neurotransmitter synthesis and transsulfuration.

B6
B6-dependent enzymes (CBS, CSE) are required to form and cleave cystathionine
Pyridoxine - essential for over 100 enzyme reactions including neurotransmitter synthesis and transsulfuration.
Enzymes

CSE (Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase)
CSE enzyme cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine
Enzyme that cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine; B6 dependent; also produces hydrogen sulfide.

CSE (Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase)
CSE cleaves cystathionine to release cysteine
Enzyme that cleaves cystathionine to produce cysteine; B6 dependent; also produces hydrogen sulfide.
Amino Acids
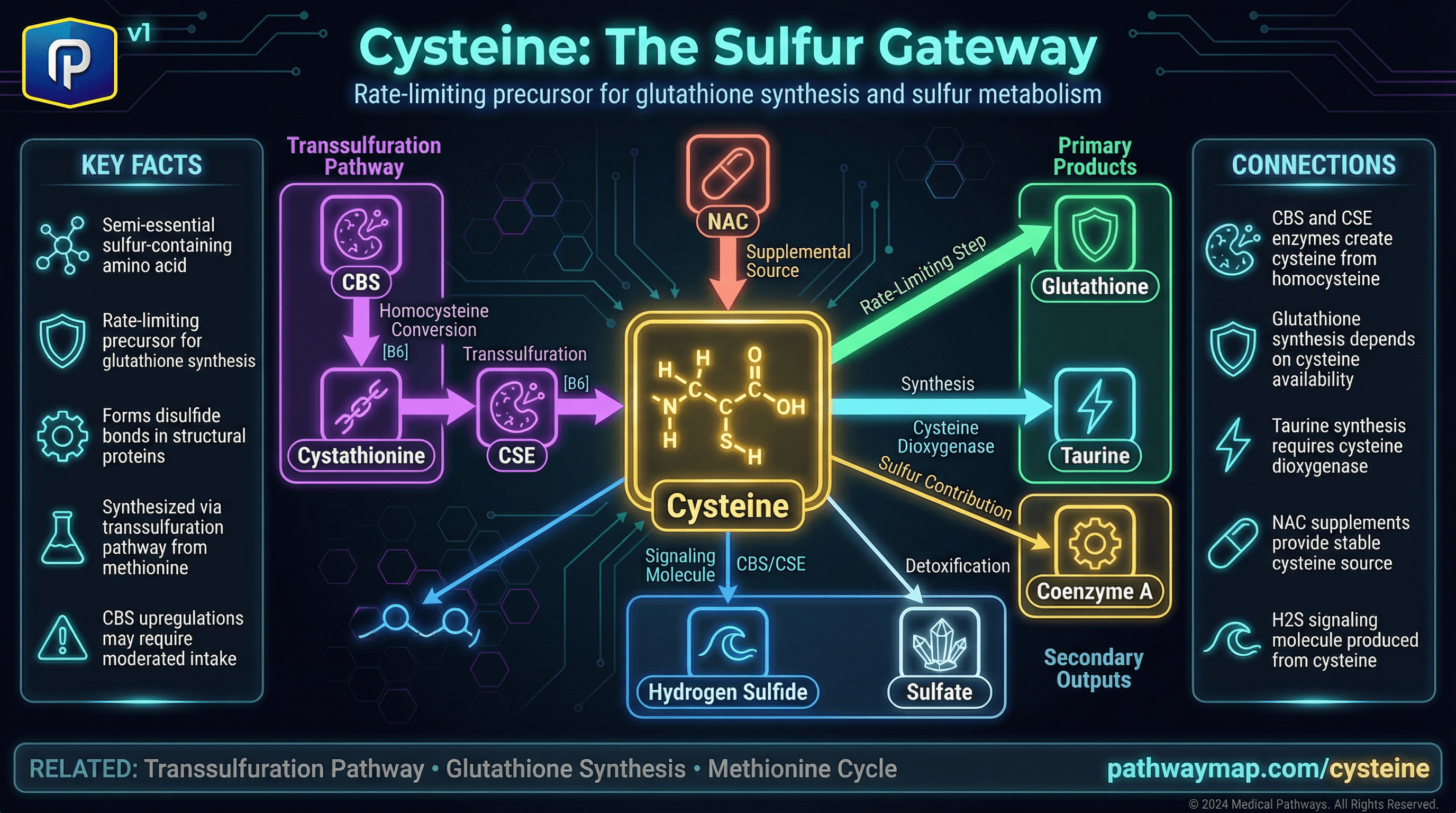
Cysteine
Cystathionine is cleaved by CSE to produce cysteine
Sulfur-containing amino acid - rate-limiting precursor for glutathione synthesis.

Cysteine
Cysteine is derived from cystathionine via CSE in transsulfuration
Sulfur-containing amino acid - rate-limiting precursor for glutathione synthesis.

Serine
Serine is combined with homocysteine by CBS to form cystathionine
Non-essential amino acid; substrate for cystathionine synthesis; precursor for glycine, sphingolipids, and phospholipids.

Serine
Serine contributes to cystathionine formation
Non-essential amino acid; substrate for cystathionine synthesis; precursor for glycine, sphingolipids, and phospholipids.
Methylation

Homocysteine
Cystathionine is formed from homocysteine via CBS enzyme
Sulfur-containing amino acid at the crossroads of methylation. Elevated levels indicate impaired methylation or B-vitamin deficiency.

Homocysteine
Homocysteine is converted to cystathionine by CBS with serine
Sulfur-containing amino acid at the crossroads of methylation. Elevated levels indicate impaired methylation or B-vitamin deficiency.

