Ribose
Five-carbon sugar; backbone of RNA and component of ATP, NAD, FAD, and CoA; supports energy recovery.
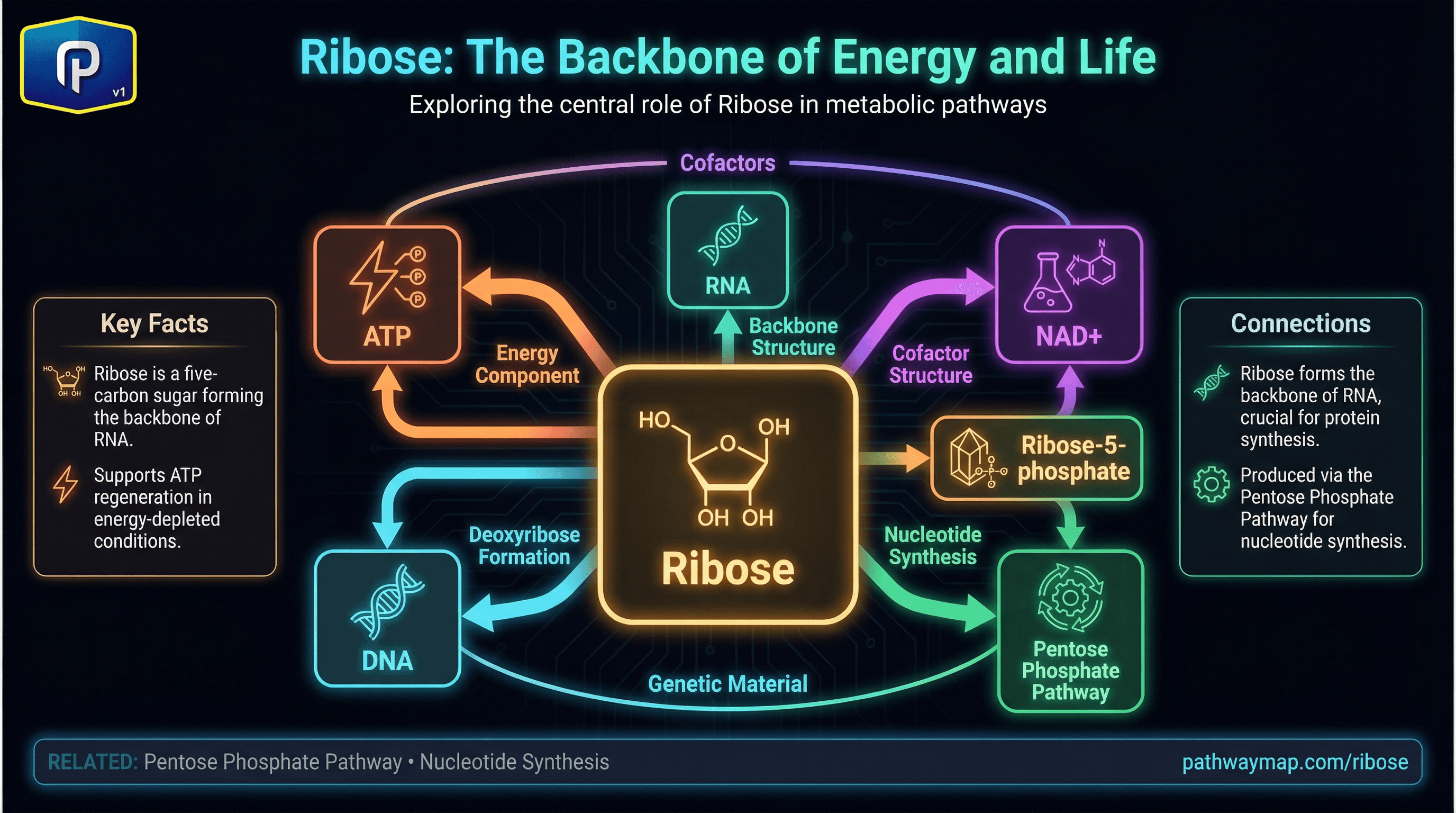
Ribose is a five-carbon sugar (pentose) that forms the backbone of RNA and is a component of important cofactors: ATP, NAD+, NADP+, FAD, and coenzyme A.
Ribose-5-phosphate is produced by the pentose phosphate pathway and is essential for nucleotide synthesis.
D-ribose supplementation has been studied for supporting ATP regeneration in conditions of energy depletion, such as heart failure, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, and intense exercise recovery. The theory is that providing ribose bypasses rate-limiting steps in nucleotide synthesis, accelerating ATP recovery.
Deoxyribose, lacking one oxygen, forms the backbone of DNA. Ribose is generally well-tolerated but can lower blood glucose in susceptible individuals.
Metabolic Connections
Ribose connects to 7 other pathways.
Cofactors

ATP
Ribose is a structural component of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate - universal energy currency of cells. Requires magnesium for biological activity.

NAD+
Ribose is part of the NAD and NADP structure
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - essential coenzyme for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and sirtuin activation.
Processes
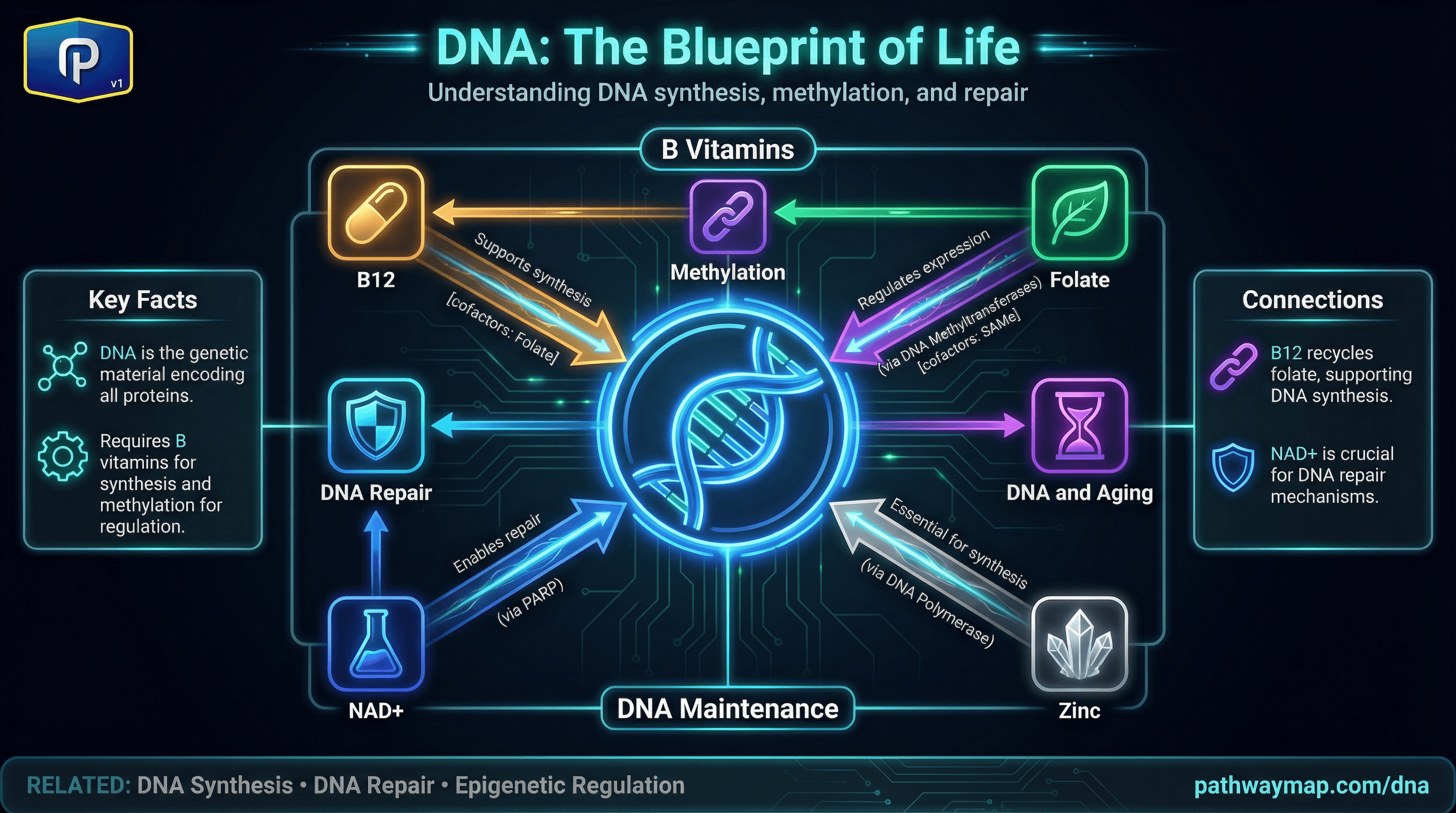
DNA
Deoxyribose (from ribose) forms the DNA backbone
Genetic material encoding all proteins. Requires B vitamins for synthesis and methylation for regulation.
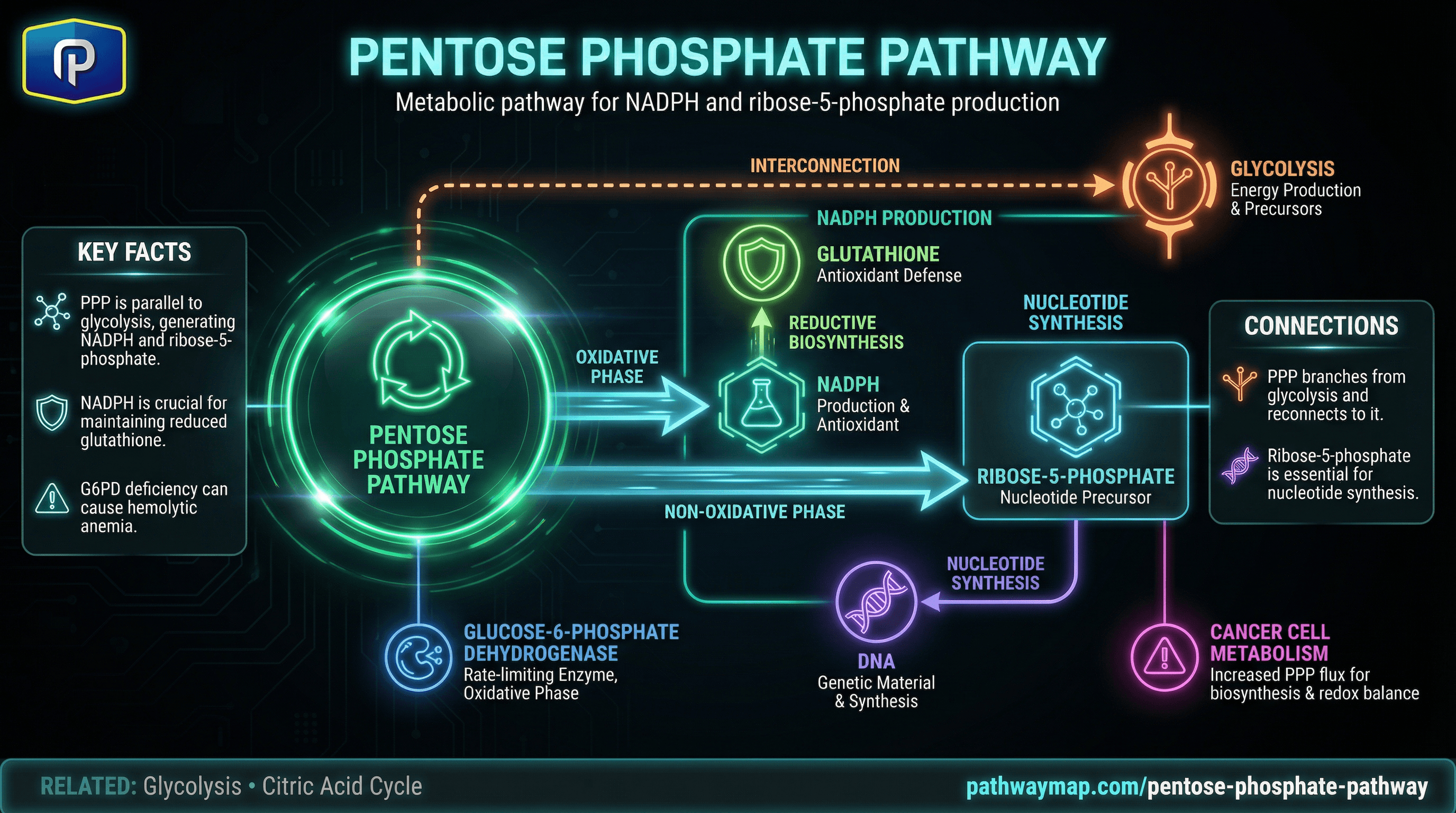
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Ribose-5-phosphate is produced by the pentose phosphate pathway
Metabolic pathway producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis; branches from glycolysis.

Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotides is produced by PPP
Metabolic pathway producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis; branches from glycolysis.
