DNA
Genetic material encoding all proteins. Requires B vitamins for synthesis and methylation for regulation.
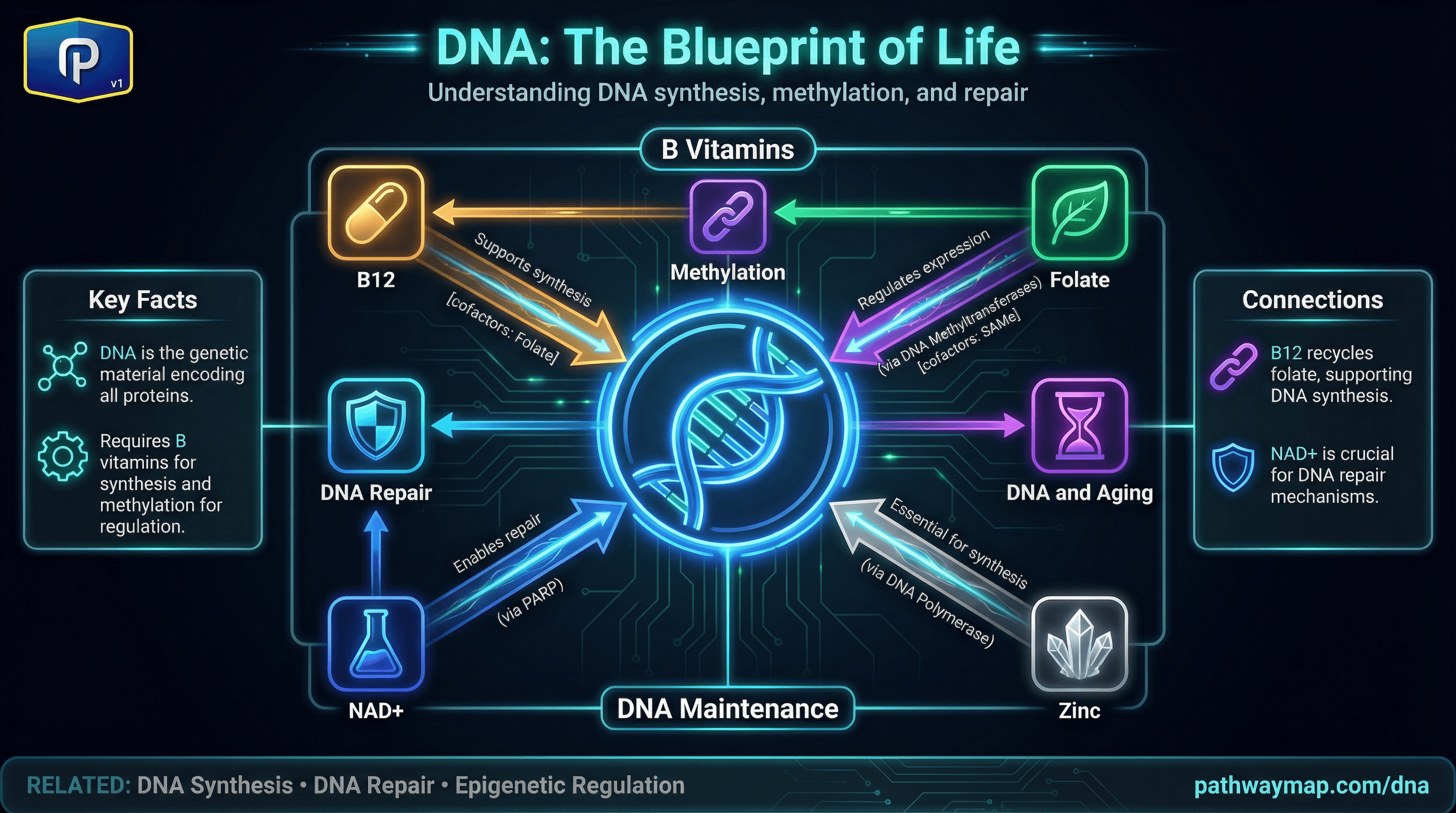
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms. It consists of two strands forming a double helix, with the sequence of nucleotide bases (A, T, G, C) encoding genetic instructions.
DNA synthesis
Nucleotides (the building blocks)
Folate (for purine and thymidine synthesis)
B12 (for folate recycling)
Zinc (for DNA polymerase)
Magnesium (cofactor for many enzymes).
DNA methylation: Methyl groups are added to cytosine bases (primarily at CpG sites) by DNA methyltransferases using SAMe. Methylation typically silences gene expression. Aberrant methylation patterns are associated with cancer and aging. Methylation patterns can be influenced by diet (methyl donors) and environment.
DNA repair: DNA is constantly damaged by oxidation, UV radiation, and other factors.
Repair mechanisms
NAD+ (for PARP enzymes)
Zinc (for repair enzymes)
B vitamins (for nucleotide synthesis)
Adequate antioxidants (to prevent damage).
DNA and aging: DNA damage accumulates with age. Telomeres (chromosome ends) shorten with each cell division. Epigenetic changes (including methylation) accumulate. Supporting DNA integrity through nutrition may slow aging: antioxidants reduce damage, B vitamins support synthesis and methylation, NAD+ supports repair.
Nutrient deficiencies affecting DNA: Folate deficiency causes DNA damage and aberrant methylation. B12 deficiency impairs folate function. Zinc deficiency impairs DNA synthesis and repair.
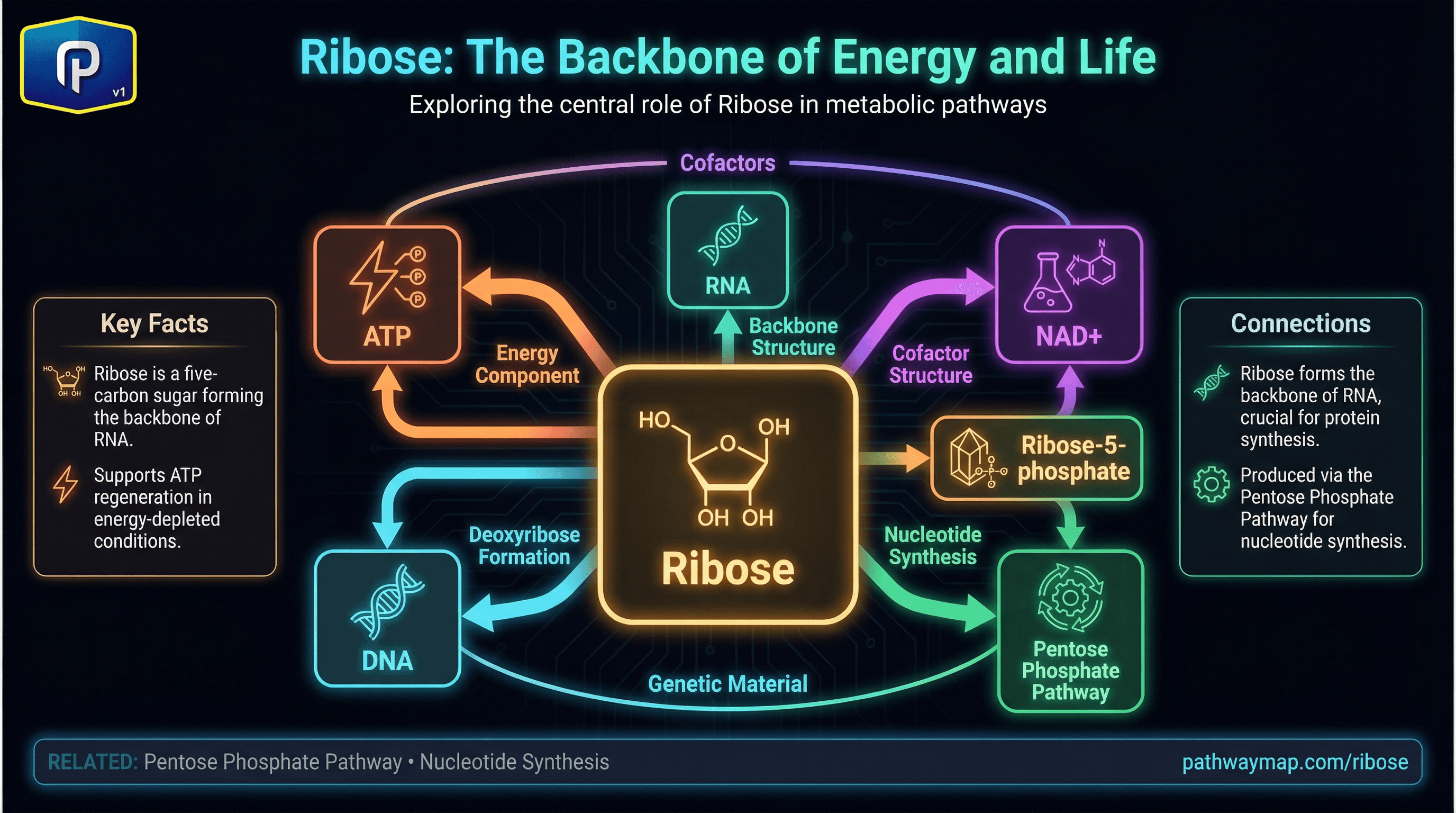
Metabolic Connections
DNA connects to 14 other pathways.
B Vitamins

B12
B12 is needed for folate recycling, supporting DNA synthesis
Cobalamin - essential for methylation, nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation.

Folate
Folate is required for DNA synthesis (nucleotide production)
Vitamin B9 - essential for DNA synthesis, methylation, and cell division. Critical during pregnancy for neural tube development.

Folate
Folate-derived one-carbon units are essential for nucleotide synthesis for DNA
Vitamin B9 - essential for DNA synthesis, methylation, and cell division. Critical during pregnancy for neural tube development.
Enzymes

DHFR (Dihydrofolate Reductase)
DHFR is essential for thymidine synthesis for DNA; its inhibition blocks DNA synthesis
Enzyme reducing dihydrofolate to THF; target of methotrexate; essential for maintaining folate pool.

PARP (Poly-ADP-Ribose Polymerase)
PARP is activated by DNA damage and facilitates repair
DNA repair enzyme consuming NAD+; overactivation depletes NAD+ and ATP; inhibited by niacinamide.
Processes

Methylation
DNA methylation is a key epigenetic mechanism controlling gene expression
Essential biochemical process transferring methyl groups for DNA regulation, neurotransmitter metabolism, detoxification, and more.

Methylation
DNA methylation is a key epigenetic mechanism regulated by the methylation cycle
Essential biochemical process transferring methyl groups for DNA regulation, neurotransmitter metabolism, detoxification, and more.
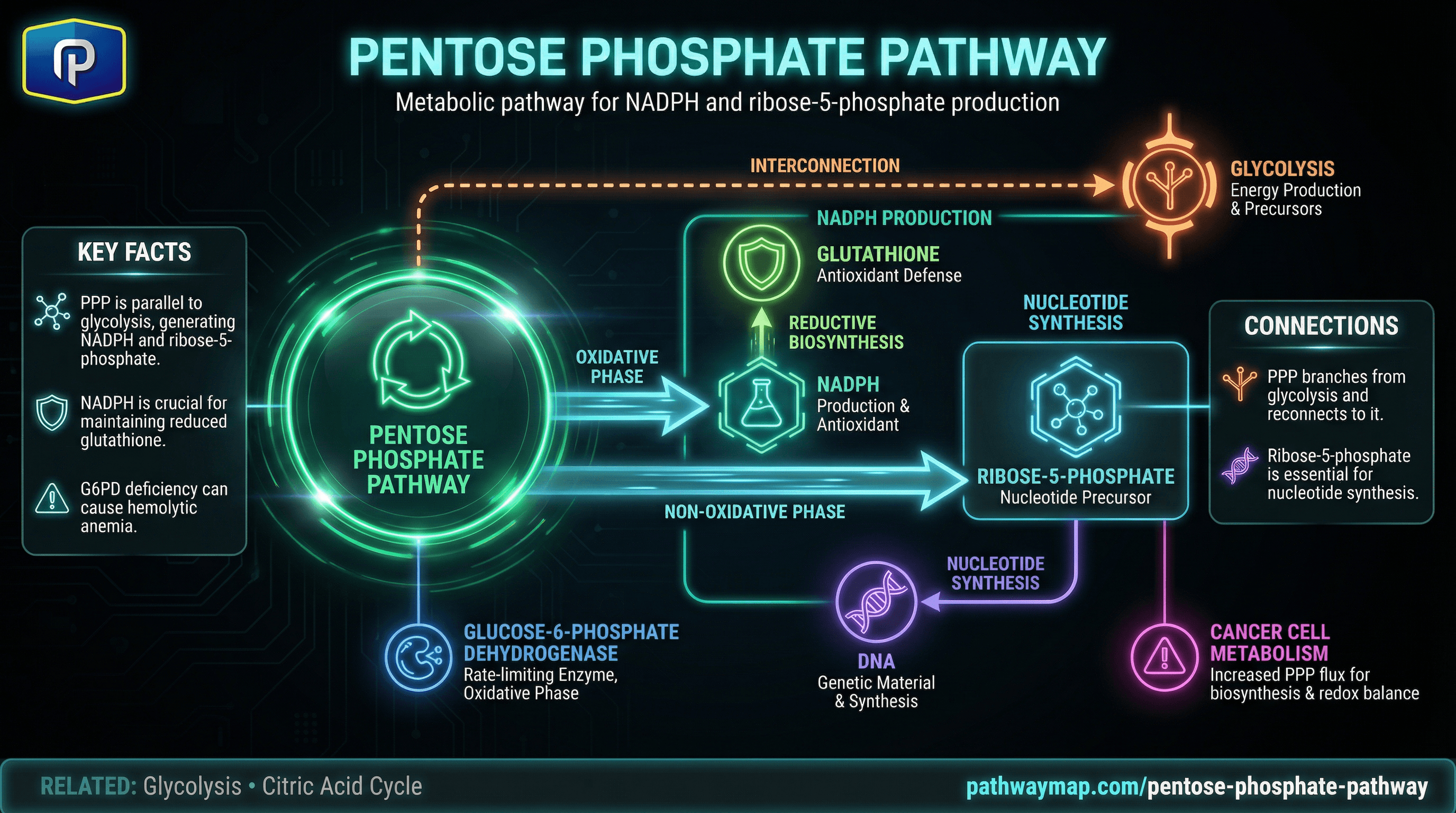
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
PPP produces ribose-5-phosphate needed for nucleotide synthesis
Metabolic pathway producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis; branches from glycolysis.
Cofactors

NAD+
NAD+ is required for PARP enzymes involved in DNA repair
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - essential coenzyme for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and sirtuin activation.

THF (Tetrahydrofolate)
THF-carried one-carbon units are essential for nucleotide synthesis for DNA
Active form of folate; carrier of one-carbon units; essential for nucleotide synthesis and methylation.
Biomolecules

Protein
DNA contains the genetic code for all proteins
Macromolecule composed of amino acids; essential for structure, enzymes, signaling, transport, and immunity.

RNA
RNA is transcribed from DNA; carries genetic information for translation
Ribonucleic acid; carries genetic information from DNA; mRNA, tRNA, rRNA essential for protein synthesis.