THF (Tetrahydrofolate)
Active form of folate; carrier of one-carbon units; essential for nucleotide synthesis and methylation.

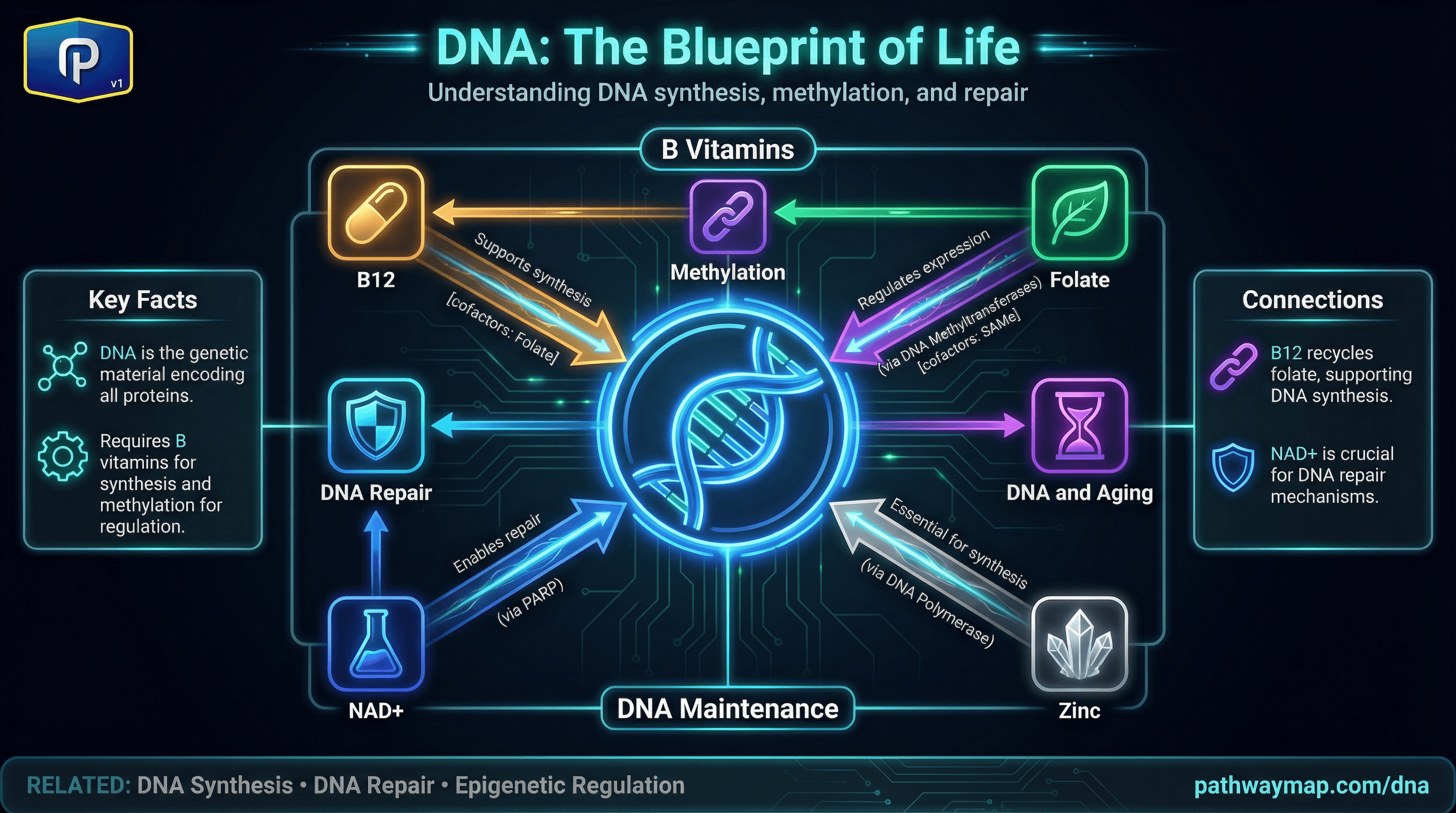
Tetrahydrofolate (THF) is the active, reduced form of folate (vitamin B9) that serves as a carrier for one-carbon units in various oxidation states. THF can accept one-carbon units from serine (via SHMT), formate, or histidine, forming various folate derivatives: 5,10-methyleneTHF, 10-formylTHF, 5-methylTHF, etc.
These one-carbon units are used for: purine and thymidine synthesis (DNA), methionine regeneration (methylation), and amino acid metabolism. The folate cycle interconverts these forms as needed. Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) reduces dietary folate and the dihydrofolate produced during thymidine synthesis back to THF.
Methotrexate inhibits DHFR, depleting THF - this is its mechanism in cancer and autoimmune disease.
Metabolic Connections
THF (Tetrahydrofolate) connects to 9 other pathways.
Enzymes

DHFR (Dihydrofolate Reductase)
DHFR reduces dihydrofolate back to THF
Enzyme reducing dihydrofolate to THF; target of methotrexate; essential for maintaining folate pool.

DHFR (Dihydrofolate Reductase)
DHFR produces THF by reducing dihydrofolate
Enzyme reducing dihydrofolate to THF; target of methotrexate; essential for maintaining folate pool.

SHMT (Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase)
SHMT transfers one-carbon units between serine/glycine and THF
Enzyme interconverting serine and glycine; major source of one-carbon units for folate pool; B6 dependent.

SHMT (Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase)
SHMT uses THF as acceptor for one-carbon unit from serine
Enzyme interconverting serine and glycine; major source of one-carbon units for folate pool; B6 dependent.
B Vitamins

Folate
THF is the active reduced form of dietary folate
Vitamin B9 - essential for DNA synthesis, methylation, and cell division. Critical during pregnancy for neural tube development.

Folate
THF is the active reduced form of folate that carries one-carbon units
Vitamin B9 - essential for DNA synthesis, methylation, and cell division. Critical during pregnancy for neural tube development.