Methylfolate (5-MTHF)
The active, methylated form of folate. Commonly recommended for MTHFR variants—but is bypassing your body's regulatory mechanisms always beneficial?
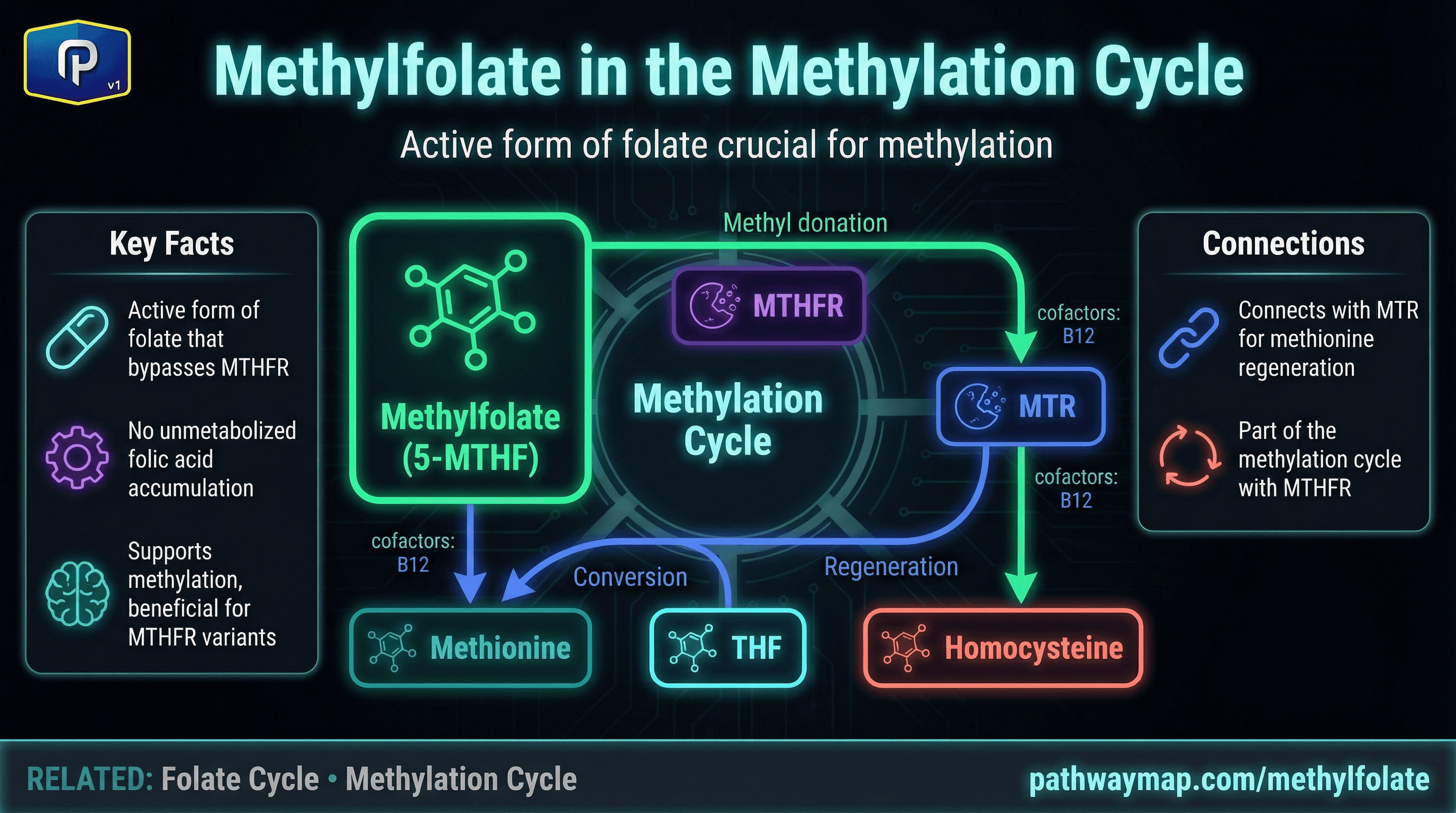
What Is Methylfolate?
5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), commonly called methylfolate, is the predominant form of folate circulating in your blood. It's the end product of the MTHFR enzyme and the form that donates methyl groups to homocysteine via the MTR (methionine synthase) enzyme.
Unlike folic acid (synthetic) or food folate, methylfolate is already in its active form. It doesn't need conversion by DHFR or MTHFR—it's ready to participate in methylation immediately.
⚠️ The Supplement Paradox
Methylfolate supplements are heavily marketed for MTHFR variants with the logic: "Your MTHFR is slow, so bypass it with the active form." This sounds reasonable—but it ignores a critical question:
What if your body slowed MTHFR on purpose?
MTHFR variants may be protective—reducing methylation (and thus oxidative stress) when your body is already under metabolic pressure from toxins, inflammation, or depleted antioxidant reserves. Forcing methylation higher with supplements may override this protective slowdown.
Many people feel worse on methylfolate—anxious, wired, overstimulated, or depressed. This isn't always a "detox reaction" or "starting dose too high." Sometimes it's your body resisting increased methylation for good reason.
Learn more: MTHFR as Purposeful Slowdown
🏭 How Methylfolate is Manufactured
Unlike natural folate from food, supplemental methylfolate requires complex chemical synthesis or biotechnological production. Understanding the manufacturing process helps explain cost differences and quality variations between products.
Manufacturing Methods
1. Chemical Synthesis (Most Common)
Commercially available 5-MTHF (like Metafolin®) is synthesized through a multi-step chemical process:
- Synthetic folic acid is reduced with sodium borohydride to produce tetrahydrofolic acid (THF)
- THF is condensed with formaldehyde to create 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
- Further reduction with sodium borohydride yields L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate
- Crystallization (often using HEM as a solvent) and purification to remove residual chemicals
Concerning Chemicals Used:
- Formaldehyde - Used to create the intermediate. EFSA testing confirms no quantifiable amounts remain in final product (<20 mg/kg or 0.002% w/w)
- Sodium Borohydride - Reducing agent. Toxic if swallowed, causes severe burns, may damage fertility or unborn child
- Platinum catalysts - Used in some synthesis methods
- HEM (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)morpholine) - Used in crystallization steps
While regulatory testing confirms these chemicals are removed to safe levels in pharmaceutical-grade products, quality varies between manufacturers. Third-party certification matters.
2. Biotechnological/Fermentation
Some manufacturers use engineered bacteria or yeast strains that produce 5-MTHF through their metabolic pathways. This approach can yield higher purity and better stereochemical selectivity without harsh chemical synthesis, but requires significant expertise in fermentation technology and is less common commercially.
Key Manufacturing Challenges
Stability Issues
Methylfolate is highly sensitive to light, heat, oxygen, and moisture. It degrades rapidly if not properly protected, making formulation and storage critical.
Stereochemistry
Only the L-form (also called 6S form) is biologically active. Manufacturing must ensure the correct isomer; the presence of D-form reduces efficacy and increases cost per active dose.
Purity Control
Synthesis can produce side products and contaminants. High-grade pharmaceutical methylfolate requires extensive purification steps (chromatography, crystallization), adding to costs.
Salt Forms
Methylfolate is typically sold as calcium salt (Metafolin®) or glucosamine salt (Quatrefolic®) to improve stability. These different forms have varying bioavailability and manufacturing complexity.
Why does this matter? Manufacturing complexity explains why methylfolate supplements are significantly more expensive than folic acid. It also means quality varies widely between brands— factors like purity, stability, and correct stereochemistry directly affect how well the supplement works. Third-party testing (USP, NSF certification) helps verify quality.
When to Consider Methylfolate (and When Not To)
May Be Helpful For:
- • Confirmed methylfolate deficiency (low RBC folate)
- • Pregnancy/neural tube defect prevention (if tolerated)
- • Depression with low folate status
- • When food folate absorption is impaired
⚠️ Important: Only after attempting to balance the general nutrients of methylation (B2, B12, magnesium, glycine, etc.) and addressing toxic burden.
Proceed With Caution:
- • High oxidative stress or depleted glutathione
- • CBS upregulation (excess sulfur pathway activity)
- • Histamine intolerance (methylation can increase histamine)
- • If you feel worse on methylfolate—listen to your body
Consider addressing upstream issues first: reduce toxic burden, support detox capacity (glutathione, NAC), ensure cofactors (B2, B12, magnesium), and support mitochondrial function before forcing methylation higher.
🪤 The Methyl Trap
The "methyl trap" occurs when B12 is deficient. Methylfolate accumulates because it can't donate its methyl group without B12-dependent MTR enzyme. This traps folate in the methylfolate form, making it unavailable for DNA synthesis and other folate-dependent reactions.
This is why supplementing methylfolate without adequate B12 is dangerous—it can mask B12 deficiency while allowing neurological damage to progress. Always ensure B12 status before high-dose methylfolate.
Metabolic Connections
MTHFR
MTHFR produces methylfolate from 5,10-methylene-THF
Vitamin B12
B12 is required for methylfolate to donate its methyl group
Homocysteine
Methylfolate provides the methyl to convert homocysteine to methionine
Methylation
Methylfolate is the primary folate form supporting methylation
Folate
Methylfolate is the primary circulating form of folate
Vitamin B2
B2 (as FAD) is required for MTHFR to produce methylfolate