Worrier or Warrior?
COMT clears dopamine, norepinephrine, and estrogens. How fast it works shapes your personality and stress response.

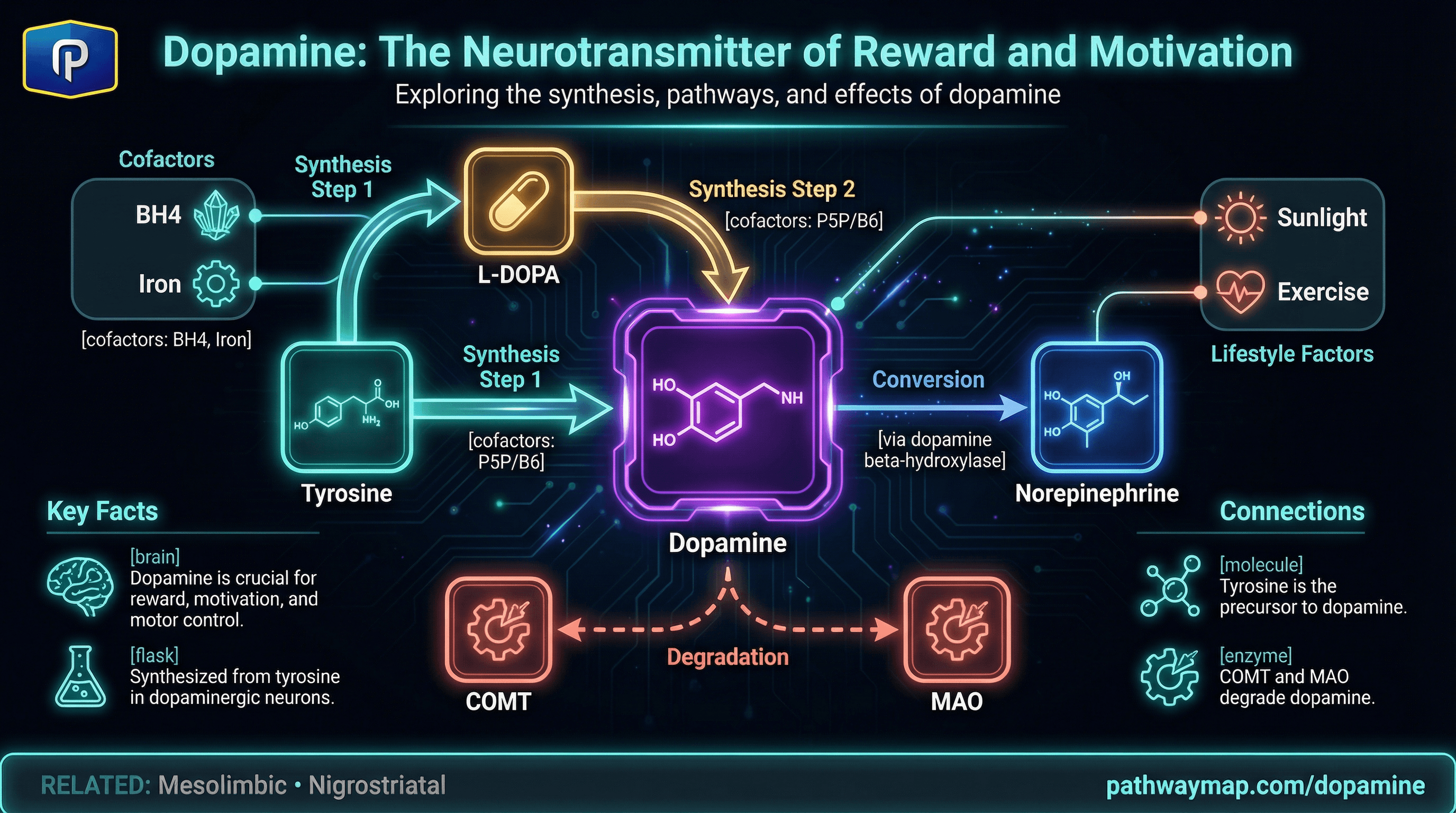
What COMT does.
COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase) adds a methyl group to catechol compounds, deactivating them.
COMT breaks down:
Dopamine
Motivation and reward
Norepinephrine
Alertness and stress
Epinephrine
Fight-or-flight
Catechol Estrogens
Estrogen metabolites
The reaction requires: SAMe (methyl donor) + Magnesium (cofactor)
The genetic variation that matters.
"Warrior"
- •Clears catecholamines quickly
- •Better stress tolerance
- •Performs well under pressure
- •May need more dopamine support
- •Can handle caffeine well
"Worrier"
- •Catecholamines linger longer
- •Better working memory and focus
- •More prone to anxiety under stress
- •Sensitive to caffeine and stimulants
- •May have estrogen clearance issues
Intermediate activity. Most common genotype. Characteristics of both.
The evolutionary trade-off.
Neither variant is "better." Each has advantages in different contexts.
Fast COMT excels at:
- • Acute stress situations
- • Physical challenges
- • Quick recovery from stress
- • Handling high-pressure deadlines
Slow COMT excels at:
- • Complex cognitive tasks
- • Attention to detail
- • Memory and learning
- • Sustained focus (in calm environments)
The key is understanding your type and optimizing your environment accordingly.
Genes don't act alone.
COMT doesn't determine your fate. It reveals where the system might need support.
Where it matters
COMT activity varies dramatically by location. In the prefrontal cortex, it's the main way dopamine is cleared. In the liver, it handles estrogen metabolites. Same gene, very different implications.
Expression depends on
- • Nutrient availability
- • Sunlight exposure
- • Toxin burden
- • Cell turnover rate
- • Age and hormonal status
SNPs are throttles, not defects
Genetic variants often slow down pathways to protect the system from overwhelm. They reveal where you need to go slower, not that you're broken.
The real question
Not "what does this gene do?" but "what is this pathway already struggling with that makes this gene relevant?"
Related patterns
"Genes don't cause outcomes. They reveal where the system is already under pressure."
Working with your COMT type.
For Fast COMT (Val/Val)
• Support dopamine: May benefit from tyrosine, adequate protein, and activities that boost dopamine
• COMT inhibitors can help: Green tea (EGCG), quercetin—slow down the enzyme
• Caffeine is usually fine: Fast clearance means less buildup
• May need more stimulation: Novelty, challenge, and reward help maintain motivation
For Slow COMT (Met/Met)
• Limit catechol sources: Reduce caffeine, wine, aged cheese, high-catechol foods
• Manage stress proactively: Catecholamines already linger—don't add more
• Avoid COMT inhibitors: Green tea, quercetin will make things worse
• Support methylation: Ensure adequate magnesium and SAMe for COMT function
• Optimize sleep: Sleep helps clear accumulated neurotransmitters
Both Types Need
Key connections.
MTHFR
Both affect methylation. MTHFR variants reduce SAMe production, which COMT needs.
Dopamine
COMT is the main way dopamine is cleared in the prefrontal cortex.
Anxiety
Slow COMT can contribute to anxiety—stress hormones linger longer.
Estrogen Dominance
Slow COMT impairs catechol estrogen clearance, potentially contributing to hormonal issues.