The molecule of more.
Dopamine isn't about pleasure. It's about wanting—the drive to pursue goals, seek rewards, and take action.
The crucial distinction.
Wanting
Dopamine creates the drive to pursue goals. The anticipation. The motivation to act. This is dopamine's main job.
Liking
The actual pleasure of reward. This involves opioids and endocannabinoids more than dopamine. Different system.
Low dopamine doesn't mean you can't enjoy things. It means you don't feel like doing anything to begin with.
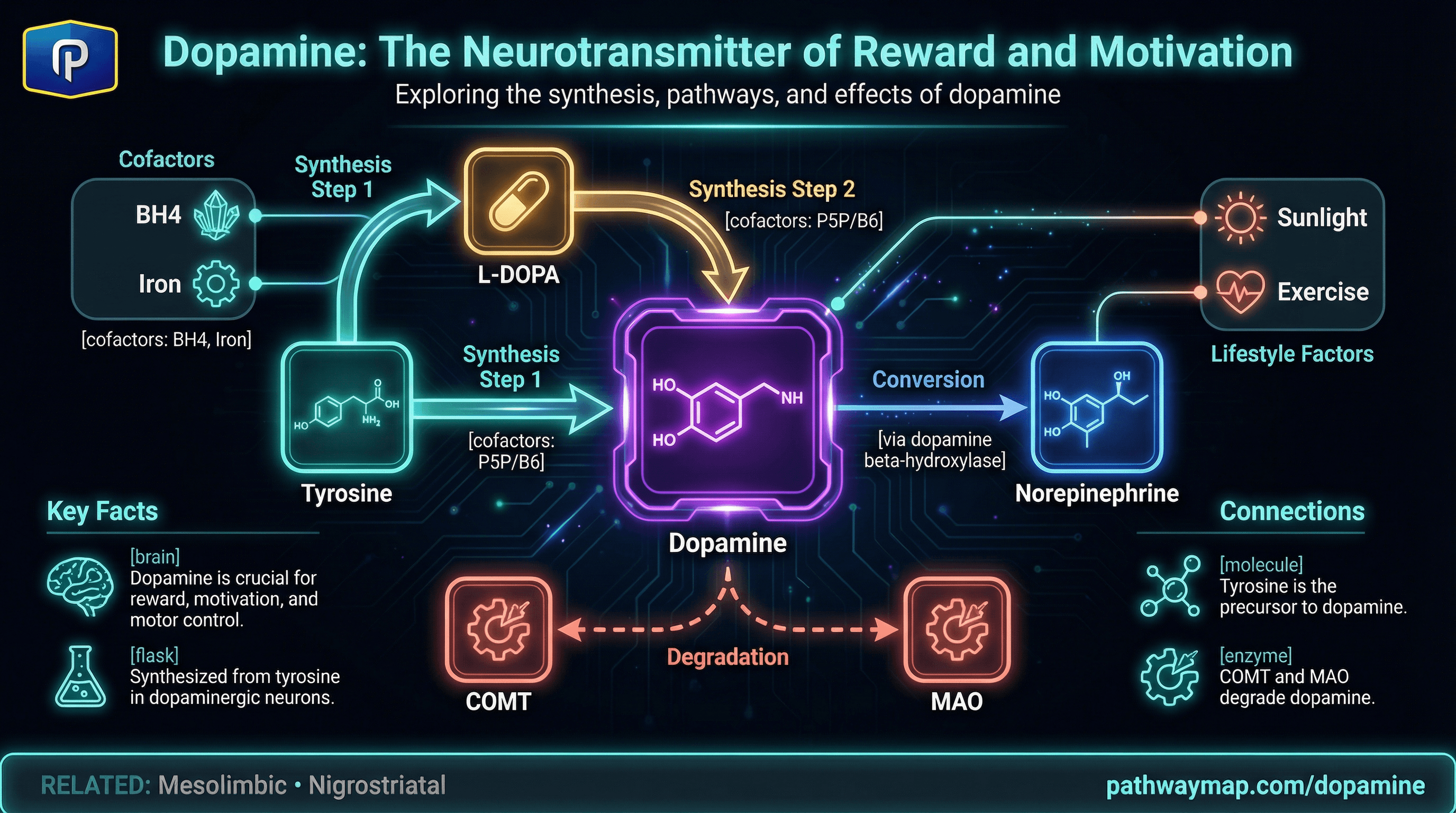
How dopamine is made.
Tyrosine
Amino acid precursor. From diet or converted from phenylalanine. Crosses blood-brain barrier.
L-DOPA
Intermediate. This is what Parkinson's patients take (levodopa) to boost dopamine.
Dopamine
Active neurotransmitter. Can be further converted to norepinephrine and epinephrine.
BH4 is rate-limiting. Tyrosine hydroxylase requires tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). Low BH4 = low dopamine production regardless of tyrosine levels. BH4 depends on folate, B12, and iron.
Four major dopamine pathways.
Mesolimbic Pathway
VTA → Nucleus Accumbens
The "reward pathway." Drives motivation, pleasure anticipation, and reinforcement learning. Hijacked by addiction.
Mesocortical Pathway
VTA → Prefrontal Cortex
Executive function, working memory, attention, and decision-making. Involved in ADHD and schizophrenia.
Nigrostriatal Pathway
Substantia Nigra → Striatum
Motor control and movement initiation. Degeneration causes Parkinson's disease symptoms.
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
Hypothalamus → Pituitary
Inhibits prolactin release. Low dopamine here = high prolactin = hormonal issues.
How dopamine is cleared.
Dopamine is inactivated by two main enzymes. Genetics affect how fast this happens.
COMT
Catechol-O-methyltransferase. Methylates dopamine using SAMe.
MAO
Monoamine oxidase. Breaks down dopamine via oxidation.
Signs of low dopamine.
How to support dopamine.
Morning Sunlight
Light exposure stimulates dopamine in the retina. 10-30 minutes of morning sun boosts dopamine levels for hours.
Exercise
Increases dopamine receptor density and synthesis. The effect is dose-dependent—more intense exercise, more dopamine.
Tyrosine
The amino acid precursor. Useful under stress when dopamine is depleted. 500-2000mg on empty stomach.
Iron
Required for tyrosine hydroxylase. Low iron = low dopamine synthesis. Common in menstruating women.
Vitamin B6
Cofactor for converting L-DOPA to dopamine. P5P form is active and doesn't require conversion.
Novel Experiences
Novelty triggers dopamine. New places, new skills, new challenges. The anticipation is the dopamine.


