Glutamate
Primary excitatory neurotransmitter and metabolic hub. Precursor to GABA and glutathione component.

Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and a central amino acid in metabolism. It sits at the intersection of energy metabolism, nitrogen handling, neurotransmission, and antioxidant synthesis. As a neurotransmitter: Glutamate mediates fast excitatory transmission via AMPA and kainate receptors, and slower signaling/plasticity via NMDA receptors (also requiring glycine and magnesium).
Excessive glutamate causes excitotoxicity - neuronal damage from overactivation, implicated in stroke, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegeneration. Metabolic roles: Glutamate is interconvertible with alpha-ketoglutarate (Krebs cycle intermediate), making it central to amino acid and energy metabolism.
It is the primary nitrogen carrier, accepting and donating amino groups in transamination reactions. Glutamate as precursor: Converted to GABA by GAD enzyme (requires B6), Incorporated into glutathione (glutamate-cysteine-glycine tripeptide), and Converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase (ammonia detoxification).
Glutamate/glutamine cycle: Astrocytes take up synaptic glutamate and convert it to glutamine, which is returned to neurons for reconversion to glutamate. This prevents excitotoxicity and recycles the neurotransmitter. Dietary glutamate (MSG, hydrolyzed proteins) doesn't normally cross the blood-brain barrier, but may cause symptoms in sensitive individuals, possibly through gut-brain signaling.
Excess glutamate relative to GABA can manifest as anxiety, insomnia, and sensory sensitivity.
Metabolic Connections
Glutamate connects to 10 other pathways.
Metabolites
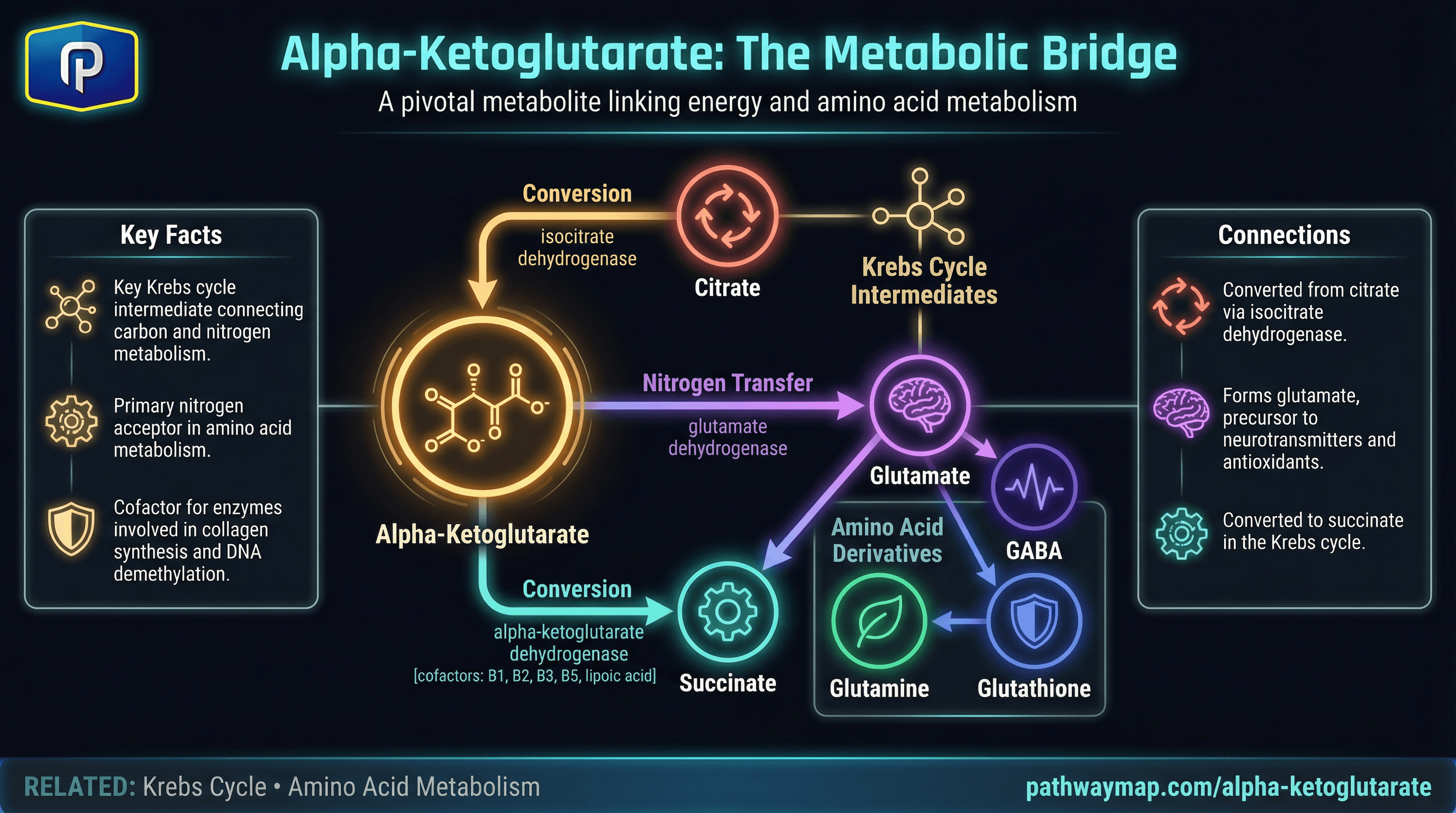
Alpha-Ketoglutarate
Glutamate can be converted to alpha-ketoglutarate by transamination or oxidative deamination
Krebs cycle intermediate bridging energy metabolism with amino acid synthesis. Precursor to glutamate.

Alpha-Ketoglutarate
Alpha-ketoglutarate combines with ammonia to form glutamate via glutamate dehydrogenase
Krebs cycle intermediate bridging energy metabolism with amino acid synthesis. Precursor to glutamate.

Ammonia
Glutamate incorporates ammonia to form glutamine
Toxic nitrogen waste from amino acid metabolism; detoxified to urea in liver; elevated in liver disease.
Neurotransmitters

GABA
Glutamate is converted to GABA by glutamate decarboxylase with B6
Gamma-aminobutyric acid - primary inhibitory neurotransmitter. Promotes calm, reduces anxiety, and supports sleep.

GABA
GABA is synthesized from glutamate by glutamate decarboxylase (requires B6)
Gamma-aminobutyric acid - primary inhibitory neurotransmitter. Promotes calm, reduces anxiety, and supports sleep.
Amino Acids

Glutamine
Glutamine is converted to glutamate by glutaminase, providing fuel and neurotransmitter precursor
Most abundant amino acid in the body. Primary fuel for intestinal cells and immune cells. Important for gut barrier integrity.

Proline
Proline is synthesized from glutamate
Non-essential amino acid; abundant in collagen; can be synthesized from glutamate; requires vitamin C for hydroxylation.
Detoxification

Glutathione
Master antioxidant and detoxifier. Tripeptide of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine essential for cellular protection.

Glutathione
Glutamate is one of three amino acids in glutathione
Master antioxidant and detoxifier. Tripeptide of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine essential for cellular protection.
