NADPH
Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; provides reducing power for biosynthesis and antioxidant defense.

NADPH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) is the primary source of reducing equivalents for biosynthetic reactions and antioxidant defense. Unlike NADH which feeds into ATP production, NADPH is used for: fatty acid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis, steroid hormone synthesis, neurotransmitter synthesis, glutathione reduction (via glutathione reductase), thioredoxin system, and xenobiotic detoxification (cytochrome P450).
NADPH is produced primarily by the pentose phosphate pathway (especially G6PD) and by malic enzyme and isocitrate dehydrogenase. G6PD deficiency causes hemolytic anemia due to inability to maintain reduced glutathione in red blood cells. NADPH oxidases use NADPH to generate reactive oxygen species for immune defense and signaling.
Metabolic Connections
NADPH connects to 11 other pathways.
B Vitamins

B3
NADPH is derived from niacin (B3) as nicotinamide component
Niacin - precursor to NAD+ and NADP+. Essential for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cell signaling.

B3
NADPH is derived from NAD phosphate; niacin supports both pools
Niacin - precursor to NAD+ and NADP+. Essential for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cell signaling.
Enzymes

Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
NADPH provides electrons for CYP450 catalytic cycle
Heme-containing enzymes metabolizing drugs, toxins, and hormones; require B vitamins, iron, and proper redox status.

DHFR (Dihydrofolate Reductase)
DHFR uses NADPH to reduce dihydrofolate to THF
Enzyme reducing dihydrofolate to THF; target of methotrexate; essential for maintaining folate pool.

DHFR (Dihydrofolate Reductase)
NADPH provides reducing equivalents for DHFR
Enzyme reducing dihydrofolate to THF; target of methotrexate; essential for maintaining folate pool.
Detoxification

Glutathione
NADPH provides reducing equivalents to regenerate reduced glutathione
Master antioxidant and detoxifier. Tripeptide of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine essential for cellular protection.

Glutathione
NADPH is required by glutathione reductase to recycle oxidized glutathione
Master antioxidant and detoxifier. Tripeptide of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine essential for cellular protection.
Cofactors

NAD+
NADPH is the phosphorylated, reduced form related to NAD metabolism
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - essential coenzyme for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and sirtuin activation.

NAD+
NADPH is produced from NAD via kinases and the pentose phosphate pathway
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - essential coenzyme for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and sirtuin activation.
Processes
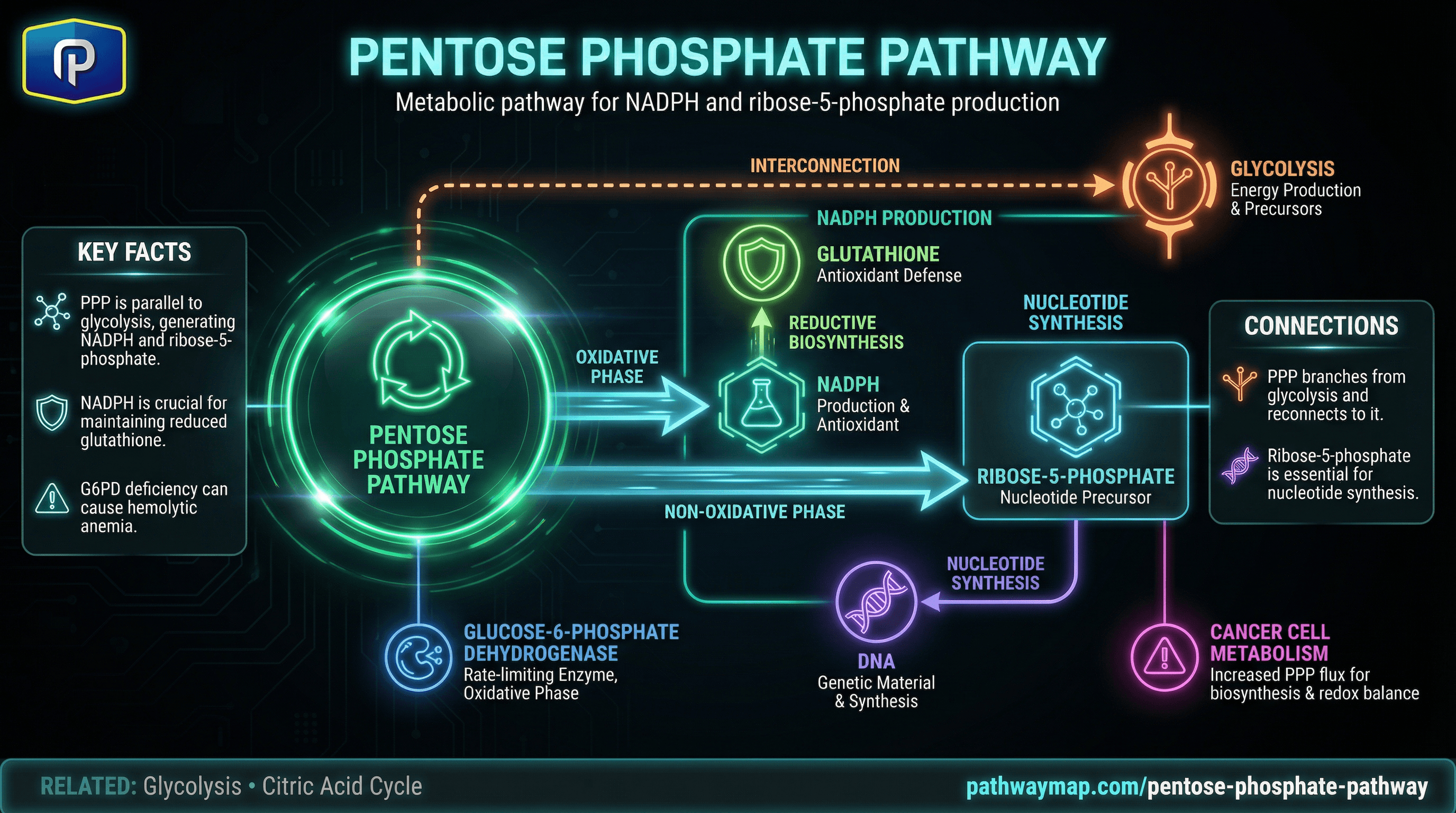
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Pentose phosphate pathway is the primary source of NADPH
Metabolic pathway producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis; branches from glycolysis.

Pentose Phosphate Pathway
PPP is the primary cellular source of NADPH
Metabolic pathway producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis; branches from glycolysis.