Sleep
The ultimate metabolic reset. During sleep, your brain clears toxins, your body repairs tissue, your hormones rebalance, and your memories consolidate. Skip it at your peril.
Sleep Architecture
Stage 1 (N1)
Light sleep. Transition from wake. Easy to wake up. 5% of night.
Stage 2 (N2)
Light-medium sleep. Heart rate drops, temp lowers. 50% of night.
Stage 3 (N3)
Deep/slow-wave sleep. Growth hormone. Physical repair. 15-20%.
REM
Dreams, memory consolidation, emotional processing. 20-25%.
What Happens While You Sleep
Glymphatic Clearance
Brain's waste system activates. Clears beta-amyloid and tau (Alzheimer's proteins). Only works during sleep.
Growth Hormone Release
70% of daily GH released during deep sleep. Repairs muscle, burns fat, regenerates tissue.
Memory Consolidation
Short-term memories transfer to long-term storage. Skills practice "replays" during REM.
Immune Restoration
Cytokine production peaks. T-cells strengthen. One bad night = 70% drop in natural killer cells.
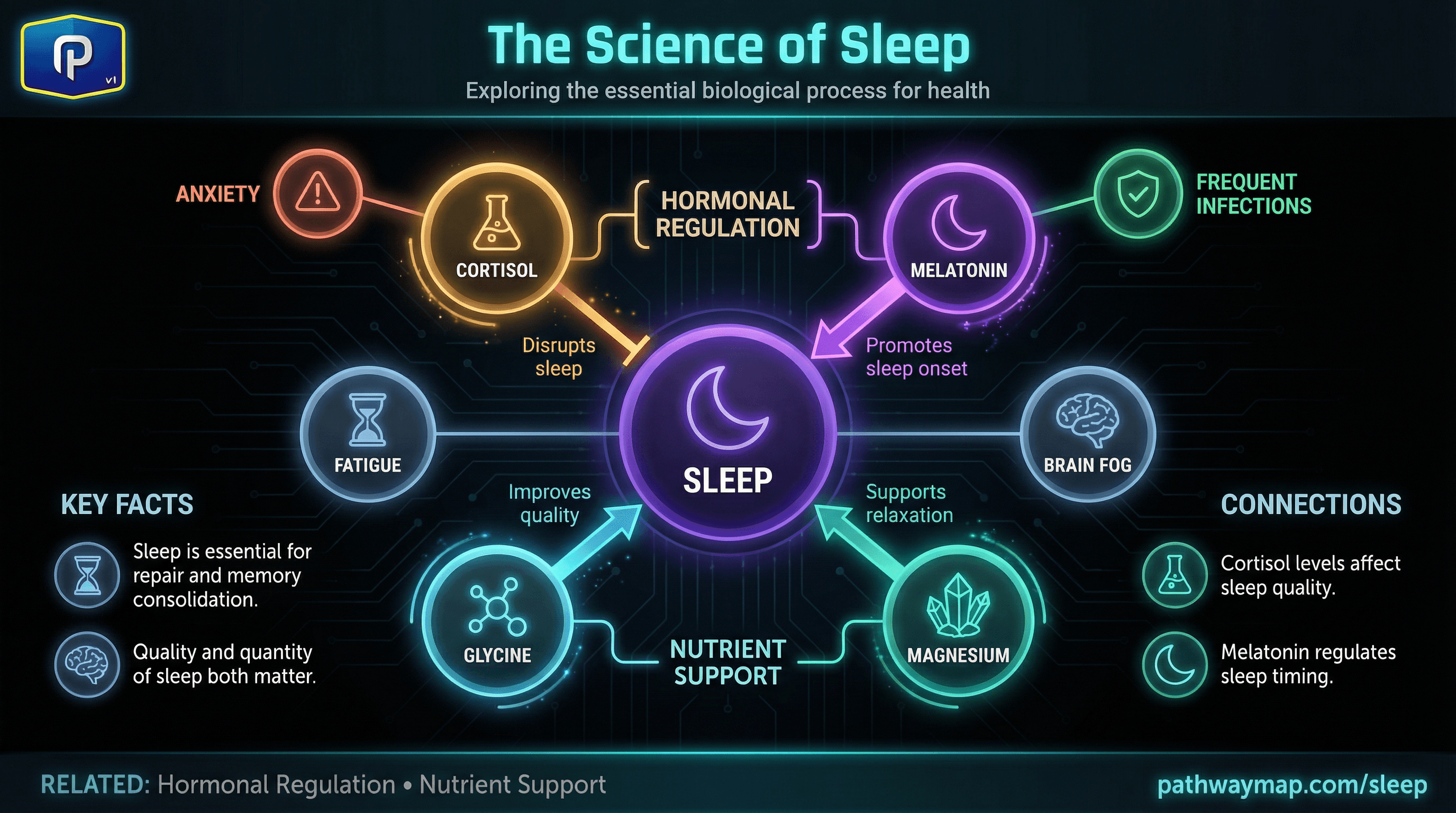
Hormone Reset
Leptin, ghrelin, insulin sensitivity, cortisol rhythm all depend on sleep quality.
Emotional Processing
REM sleep processes emotional experiences. Strips emotional charge from memories.
⚠️ What Destroys Sleep
Blue Light at Night
Screens suppress melatonin for 2-3 hours. Signals "daytime" to your brain.
Late Caffeine
Half-life of 5-6 hours. Afternoon coffee still in your system at bedtime. Blocks adenosine.
Alcohol
Sedation ≠ sleep. Fragments sleep architecture, blocks REM, causes early waking.
Irregular Schedule
Social jetlag. Different bed/wake times confuse circadian rhythm.
Room Too Warm
Body needs to drop 1-2°F to initiate sleep. Keep room 65-68°F.
Late Heavy Meals
Digestion keeps body too active. Insulin spike disrupts hormones.
Stress & Rumination
Cortisol stays elevated. Racing mind prevents relaxation.
Light Pollution
Any light in bedroom suppresses melatonin. Use blackout curtains.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Low magnesium, B6, zinc, vitamin D all impair sleep quality.
The Cost of Sleep Deprivation
Cognitive
- • Poor concentration
- • Memory problems
- • Slow reaction time
- • Impaired judgment
Metabolic
- • Insulin resistance
- • Increased hunger (ghrelin up)
- • Weight gain
- • Pre-diabetic markers after days
Immune
- • 4x more likely to catch cold
- • Reduced vaccine response
- • Increased inflammation
Emotional
- • Irritability
- • Anxiety
- • Depression risk increases
- • Emotional reactivity
Cardiovascular
- • Higher blood pressure
- • Increased heart disease risk
- • Higher stroke risk
Hormonal
- • Testosterone drops 10-15%
- • Cortisol stays elevated
- • Thyroid function impaired
✅ Sleep Optimization
Morning Sunlight
10+ minutes of bright light within 1 hour of waking. Sets circadian rhythm, starts melatonin timer.
Consistent Schedule
Same bed and wake time, even weekends. Your circadian clock craves consistency.
Cool, Dark, Quiet
65-68°F room. Blackout curtains. White noise if needed. Cave-like environment.
No Screens Before Bed
Blue light blocking glasses or no screens 1-2 hours before bed. Dim lights in evening.
Magnesium
300-400mg glycinate or threonate before bed. Calms nervous system, supports GABA.
No Late Caffeine
Cutoff at noon or 2pm. Caffeine has 5-6 hour half-life—it's still in you at bedtime.
Metabolic Connections
Melatonin
The darkness hormone that initiates sleep
Cortisol
Should be low at night, high in morning—opposite of melatonin
Magnesium
Calms the nervous system, supports GABA and melatonin
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitter that quiets brain activity
Dopamine
Screens and stimulation keep dopamine high, blocking sleep
Vitamin D
Vitamin D receptors in sleep centers—deficiency disrupts sleep